Alveologenesis: key cellular players and fibroblast growth factor 10 signaling
- PMID: 27098664
- PMCID: PMC4840179
- DOI: 10.1186/s40348-016-0045-7
Alveologenesis: key cellular players and fibroblast growth factor 10 signaling
Abstract
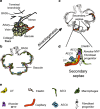
Background: Alveologenesis is the last stage in lung development and is essential for building the gas-exchanging units called alveoli. Despite intensive lung research, the intricate crosstalk between mesenchymal and epithelial cell lineages during alveologenesis is poorly understood. This crosstalk contributes to the formation of the secondary septae, which are key structures of healthy alveoli.
Conclusions: A better understanding of the cellular and molecular processes underlying the formation of the secondary septae is critical for the development of new therapies to protect or regenerate the alveoli. This review summarizes briefly the alveologenesis process in mouse and human. Further, it discusses the current knowledge on the epithelial and mesenchymal progenitor cells during early lung development giving rise to the key cellular players (e.g., alveolar epithelial cell type I, alveolar epithelial cell type II, alveolar myofibroblast, lipofibroblast) involved in alveologenesis. This review focusses mainly on the role of fibroblast growth factor 10 (FGF10), one of the most important signaling molecules during lung development, in epithelial and mesenchymal cell lineage formation.
Keywords: Alveolar epithelial cell type I (AEC I); Alveolar epithelial cell type II (AEC II); Alveolar myofibroblast; Alveologenesis; Fibroblast growth factor 10 (FGF10); Secondary septae.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

