The Medial Orbitofrontal Cortex Regulates Sensitivity to Outcome Value
- PMID: 27098701
- PMCID: PMC4837686
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4253-15.2016
The Medial Orbitofrontal Cortex Regulates Sensitivity to Outcome Value
Abstract
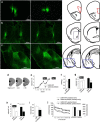
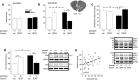
An essential component of goal-directed decision-making is the ability to maintain flexible responding based on the value of a given reward, or "reinforcer." The medial orbitofrontal cortex (mOFC), a subregion of the ventromedial prefrontal cortex, is uniquely positioned to regulate this process. We trained mice to nose poke for food reinforcers and then stimulated this region using CaMKII-driven Gs-coupled designer receptors exclusively activated by designer drugs (DREADDs). In other mice, we silenced the neuroplasticity-associated neurotrophin brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Activation of Gs-DREADDs increased behavioral sensitivity to reinforcer devaluation, whereas Bdnf knockdown blocked sensitivity. These changes were accompanied by modifications in breakpoint ratios in a progressive ratio task, and they were recapitulated in Bdnf(+/-)mice. Replacement of BDNF selectively in the mOFC in Bdnf(+/-)mice rescued behavioral deficiencies, as well as phosphorylation of extracellular-signal regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2). Thus, BDNF expression in the mOFC is both necessary and sufficient for the expression of typical effort allocation relative to an anticipated reinforcer. Additional experiments indicated that expression of the immediate-early gene c-fos was aberrantly elevated in the Bdnf(+/-)dorsal striatum, and BDNF replacement in the mOFC normalized expression. Also, systemic administration of an MAP kinase kinase inhibitor increased breakpoint ratios, whereas the addition of discrete cues bridging the response-outcome contingency rescued breakpoints in Bdnf(+/-)mice. We argue that BDNF-ERK1/2 in the mOFC is a key regulator of "online" goal-directed action selection.
Significance statement: Goal-directed response selection often involves predicting the consequences of one's actions and the value of potential payoffs. Lesions or chemogenetic inactivation of the medial orbitofrontal cortex (mOFC) in rats induces failures in retrieving outcome identity memories (Bradfield et al., 2015), suggesting that the healthy mOFC serves to access outcome value information when it is not immediately observable and thereby guide goal-directed decision-making. Our findings suggest that the mOFC also bidirectionally regulates effort allocation for a given reward and that expression of the neurotrophin BDNF in the mOFC is both necessary and sufficient for mice to sustain stable representations of reinforcer value.
Keywords: cue; dorsal striatum; neurotrophin; operant; orbital; progressive ratio.
Copyright © 2016 the authors 0270-6474/16/364600-14$15.00/0.
Figures

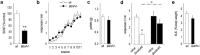


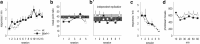


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
