ERK1/2, MEK1/2 and p38 downstream signalling molecules impaired in CD56 dim CD16+ and CD56 bright CD16 dim/- natural killer cells in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome/Myalgic Encephalomyelitis patients
- PMID: 27098723
- PMCID: PMC4839077
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-016-0859-z
ERK1/2, MEK1/2 and p38 downstream signalling molecules impaired in CD56 dim CD16+ and CD56 bright CD16 dim/- natural killer cells in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome/Myalgic Encephalomyelitis patients
Abstract
Background: Natural Killer (NK) cell effector functions are dependent on phosphorylation of the mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) pathway to produce an effective immune response for the clearance of target cells infected with viruses, bacteria or malignantly transformed cells. Intracellular signals activating NK cell cytokine production and cytotoxic activity are propagated through protein phosphorylation of MAPKs including MEK1/2, ERK1/2, p38 and JNK. Reduced NK cell cytotoxic activity is consistently reported in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome/Myalgic Encephalomyelitis (CFS/ME) patients and intracellular signalling by MAPK in NK cells remains to be investigated. Therefore, the purpose of this paper was to investigate MAPK downstream signalling molecules in NK cell phenotypes from CFS/ME patients.
Methods: Flow cytometric protocols were used to measure phosphorylation of the MAPK pathway in CD56(bright)CD16(dim/-) and CD56(dim)CD16(+) NK cells following stimulation with K562 tumour cells or phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate plus ionomycin. NK cell cytotoxic activity, degranulation, lytic proteins and cytokine production were also measured as markers for CD56(bright)CD16(dim/-) and CD56(dim)CD16(+) NK cell function using flow cytometric protocols.
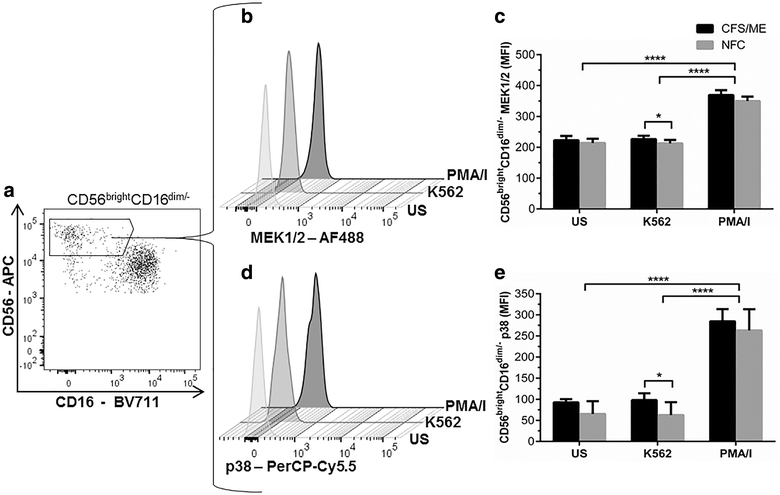
Results: CFS/ME patients (n = 14) had a significant decrease in ERK1/2 in CD56(dim)CD16(+) NK cells compared to the non-fatigued controls (n = 11) after incubation with K562 cells. CD56(bright)CD16(dim/-) NK cells from CFS/ME patients had a significant increase in MEK1/2 and p38 following incubation with K562 cells.
Conclusions: This is the first study to report significant differences in MAPK intracellular signalling molecules in CD56(dim)CD16(+) and CD56(bright)CD16(dim/-) NK cells from CFS/ME patients. The current results highlight the importance of intracellular signalling through the MAPK pathway for synergistic effector function of CD56(dim)CD16(+) and CD56(bright)CD16(dim/-) NK cells to ensure efficient clearance of target cells. In CFS/ME patients, dysfunctional MAPK signalling may contribute to reduced NK cell cytotoxic activity.
Keywords: Chronic Fatigue Syndrome/Myalgic Encephalomyelitis; Cytokine; Cytotoxic; Intracellular signalling; Mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling; Natural killer.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Impaired calcium mobilization in natural killer cells from chronic fatigue syndrome/myalgic encephalomyelitis patients is associated with transient receptor potential melastatin 3 ion channels.Clin Exp Immunol. 2017 Feb;187(2):284-293. doi: 10.1111/cei.12882. Epub 2016 Nov 23. Clin Exp Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27727448 Free PMC article.
-
Pilot Study of Natural Killer Cells in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome/Myalgic Encephalomyelitis and Multiple Sclerosis.Scand J Immunol. 2016 Jan;83(1):44-51. doi: 10.1111/sji.12388. Scand J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26381393
-
Characterisation of cell functions and receptors in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome/Myalgic Encephalomyelitis (CFS/ME).BMC Immunol. 2015 Jun 2;16:35. doi: 10.1186/s12865-015-0101-4. BMC Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26032326 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of natural killer cells profile and cytotoxic function in myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome.Syst Rev. 2019 Nov 14;8(1):279. doi: 10.1186/s13643-019-1202-6. Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31727160 Free PMC article.
-
Role of chemokines in the biology of natural killer cells.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2010;341:37-58. doi: 10.1007/82_2010_20. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20369317 Review.
Cited by
-
The effect of IL-2 stimulation and treatment of TRPM3 on channel co-localisation with PIP2 and NK cell function in myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome patients.J Transl Med. 2021 Jul 15;19(1):306. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-02974-4. J Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34266470 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Implications of Mammalian Transient Receptor Potential Melastatin 7 in the Pathophysiology of Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome: A Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Oct 12;18(20):10708. doi: 10.3390/ijerph182010708. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34682454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A targeted genome association study examining transient receptor potential ion channels, acetylcholine receptors, and adrenergic receptors in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome/Myalgic Encephalomyelitis.BMC Med Genet. 2016 Nov 11;17(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s12881-016-0342-y. BMC Med Genet. 2016. PMID: 27835969 Free PMC article.
-
Association of biomarkers with health-related quality of life and history of stressors in myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome patients.J Transl Med. 2016 Aug 31;14(1):251. doi: 10.1186/s12967-016-1010-x. J Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27580693 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of Protein Kinase Gene Expression in NK Cells from Chronic Fatigue Syndrome/Myalgic Encephalomyelitis Patients.Gene Regul Syst Bio. 2016 Aug 28;10:85-93. doi: 10.4137/GRSB.S40036. eCollection 2016. Gene Regul Syst Bio. 2016. PMID: 27594784 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

