Impact of the gut microbiota on inflammation, obesity, and metabolic disease
- PMID: 27098727
- PMCID: PMC4839080
- DOI: 10.1186/s13073-016-0303-2
Impact of the gut microbiota on inflammation, obesity, and metabolic disease
Abstract
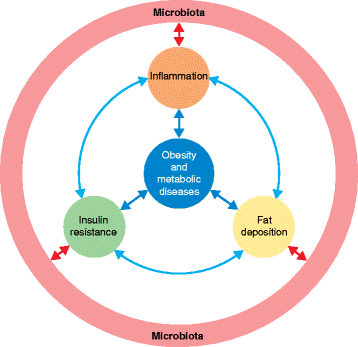
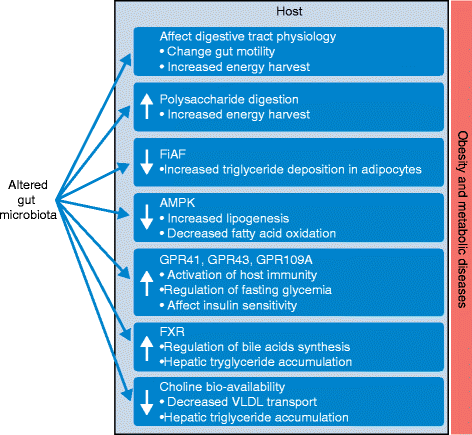
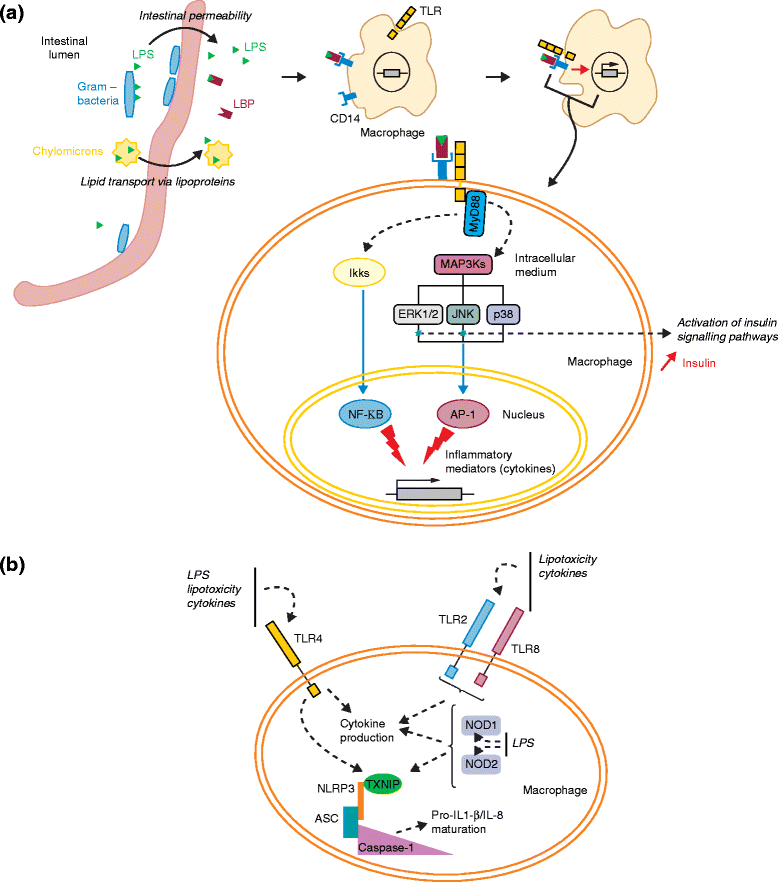
The human gut harbors more than 100 trillion microbial cells, which have an essential role in human metabolic regulation via their symbiotic interactions with the host. Altered gut microbial ecosystems have been associated with increased metabolic and immune disorders in animals and humans. Molecular interactions linking the gut microbiota with host energy metabolism, lipid accumulation, and immunity have also been identified. However, the exact mechanisms that link specific variations in the composition of the gut microbiota with the development of obesity and metabolic diseases in humans remain obscure owing to the complex etiology of these pathologies. In this review, we discuss current knowledge about the mechanistic interactions between the gut microbiota, host energy metabolism, and the host immune system in the context of obesity and metabolic disease, with a focus on the importance of the axis that links gut microbes and host metabolic inflammation. Finally, we discuss therapeutic approaches aimed at reshaping the gut microbial ecosystem to regulate obesity and related pathologies, as well as the challenges that remain in this area.
Figures

References
-
- Bruzzese E, Volpicelli M, Squaglia M, Tartaglione A, Guarino A. Impact of prebiotics on human health. Dig Liver Dis. 2006;38(Suppl 2):S283–7. doi:S1590-8658(07)60011-5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

