Mechanism and regulation of DNA end resection in eukaryotes
- PMID: 27098756
- PMCID: PMC4957645
- DOI: 10.3109/10409238.2016.1172552
Mechanism and regulation of DNA end resection in eukaryotes
Abstract
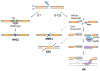
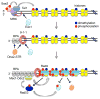
The repair of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) by homologous recombination (HR) is initiated by nucleolytic degradation of the 5'-terminated strands in a process termed end resection. End resection generates 3'-single-stranded DNA tails, substrates for Rad51 to catalyze homologous pairing and DNA strand exchange, and for activation of the DNA damage checkpoint. The commonly accepted view is that end resection occurs by a two-step mechanism. In the first step, Sae2/CtIP activates the Mre11-Rad50-Xrs2/Nbs1 (MRX/N) complex to endonucleolytically cleave the 5'-terminated DNA strands close to break ends, and in the second step Exo1 and/or Dna2 nucleases extend the resected tracts to produce long 3'-ssDNA-tailed intermediates. Initiation of resection commits a cell to repair a DSB by HR because long ssDNA overhangs are poor substrates for non-homologous end joining (NHEJ). Thus, the initiation of end resection has emerged as a critical control point for repair pathway choice. Here, I review recent studies on the mechanism of end resection and how this process is regulated to ensure the most appropriate repair outcome.
Keywords: DNA repair; Dna2; Exo1; Mre11; Sae2/CtIP; double-strand break; end joining; recombination.
Figures
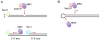

References
-
- Symington LS, Gautier J. Double-strand break end resection and repair pathway choice. Annu Rev Genet. 2011;45:247–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
