Generation of a monoclonal antibody recognizing the CEACAM glycan structure and inhibiting adhesion using cancer tissue-originated spheroid as an antigen
- PMID: 27098764
- PMCID: PMC4838943
- DOI: 10.1038/srep24823
Generation of a monoclonal antibody recognizing the CEACAM glycan structure and inhibiting adhesion using cancer tissue-originated spheroid as an antigen
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Generation of a monoclonal antibody recognizing the CEACAM glycan structure and inhibiting adhesion using cancer tissue-originated spheroid as an antigen.Sci Rep. 2016 May 31;6:26575. doi: 10.1038/srep26575. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27241769 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
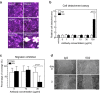
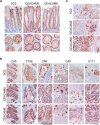
Spheroids cultured directly from tumours can better reflect in vivo tumour characteristics than two-dimensional monolayer culture or three-dimensional culture of established cell lines. In this study, we generated antibodies by directly immunizing mice with primary-cultured living spheroids from human colorectal cancer. We performed phenotypic screening via recognition of the surface of the spheroids and inhibition of their adhesion to extracellular matrices to identify a monoclonal antibody, clone 5G2. The antibody inhibited cell migration in two-dimensional culture and promoted cell detachment. Western blotting and immunohistochemistry detected the 5G2 signal in many colorectal cancer spheroids, as well as patient tumours, but failed to detect in various cell lines examined. We found that 5G2 recognized the Le(a) and Le(c) on N-glycan, and their major carrier proteins were CEACAM5 and CEACAM6. Pre-incubation of the spheroids with 5G2 impaired translocation of integrin β4 from the lateral membrane to the contact interface between the extracellular matrix when embedded in it. As we successfully obtained a functional antibody, which antigen was glycan structures and lost in cell lines, cancer tissue-originated spheroids can be a useful antigen for generating novel anti-cancer antibodies.
Figures





References
-
- Weigelt B., Lo A. T., Park C. C., Gray J. W. & Bissell M. J. HER2 signaling pathway activation and response of breast cancer cells to HER2-targeting agents is dependent strongly on the 3D microenvironment. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 122, 35–43, doi: 10.1007/s10549-009-0502-2 (2010). - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

