Population and Functional Genomics of Neisseria Revealed with Gene-by-Gene Approaches
- PMID: 27098959
- PMCID: PMC4963508
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00301-16
Population and Functional Genomics of Neisseria Revealed with Gene-by-Gene Approaches
Abstract
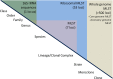
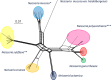
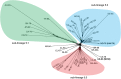
Rapid low-cost whole-genome sequencing (WGS) is revolutionizing microbiology; however, complementary advances in accessible, reproducible, and rapid analysis techniques are required to realize the potential of these data. Here, investigations of the genus Neisseria illustrated the gene-by-gene conceptual approach to the organization and analysis of WGS data. Using the gene and its link to phenotype as a starting point, the BIGSdb database, which powers the PubMLST databases, enables the assembly of large open-access collections of annotated genomes that provide insight into the evolution of the Neisseria, the epidemiology of meningococcal and gonococcal disease, and mechanisms of Neisseria pathogenicity.
Copyright © 2016 Maiden and Harrison.
Figures


References
-
- Kyrpides NC, Hugenholtz P, Eisen JA, Woyke T, Goker M, Parker CT, Amann R, Beck BJ, Chain PSG, Chun J, Colwell RR, Danchin A, Dawyndt P, Dedeurwaerdere T, DeLong EF, Detter JC, De Vos P, Donohue TJ, Dong XZ, Ehrlich DS, Fraser C, Gibbs R, Gilbert J, Gilna P, Glockner FO, Jansson JK, Keasling JD, Knight R, Labeda D, Lapidus A, Lee JS, Li WJ, Ma JC, Markowitz V, Moore ERB, Morrison M, Meyer F, Nelson KE, Ohkuma M, Ouzounis CA, Pace N, Parkhill J, Qin N, Rossello-Mora R, Sikorski J, Smith D, Sogin M, Stevens R, Stingl U, Suzuki K, et al. 2014. Genomic encyclopedia of bacteria and archaea: sequencing a myriad of type strains. PloS Biol 12:e1001920. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001920. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Maiden MCJ, Bygraves JA, Feil E, Morelli G, Russell JE, Urwin R, Zhang Q, Zhou J, Zurth K, Caugant DA, Feavers IM, Achtman M, Spratt BG. 1998. Multilocus sequence typing: a portable approach to the identification of clones within populations of pathogenic microorganisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:3140–3145. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.6.3140. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

