Epidemiology of Invasive Group B Streptococcal Disease in Alberta, Canada, from 2003 to 2013
- PMID: 27098960
- PMCID: PMC4922093
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00355-16
Epidemiology of Invasive Group B Streptococcal Disease in Alberta, Canada, from 2003 to 2013
Erratum in
-
Correction for Alhhazmi et al., Epidemiology of Invasive Group B Streptococcal Disease in Alberta, Canada, from 2003 to 2013.J Clin Microbiol. 2016 Dec 28;55(1):342-343. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02052-16. Print 2017 Jan. J Clin Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 28031447 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
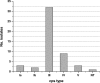
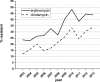
Group B streptococci (GBS) cause severe invasive disease in both neonates and adults. Understanding the epidemiology of GBS provides information that can include determining disease prevalence rates in defined populations and geographic regions, documenting the success of GBS screening programs, and understanding antimicrobial susceptibility patterns. In Alberta, only neonatal invasive GBS (iGBS) disease is notifiable to health authorities. We performed a surveillance study of iGBS in Alberta, Canada, from 2003 to 2013. Over the 11-year period, the disease incidence rate increased from a low of 3.92 cases/100,000 population to a high of 5.99 cases/100,000 population. The capsular polysaccharide serotypes (CPSs) found were CPS III (20.3%), CPS V (19.1%), CPS Ia (18.9%), CPS Ib (12.7%), CPS II (11.1%), CPS IV (6.3%), and nontypeable GBS (9.4%). Rates of early-onset disease (0 to 7 days) increased from 0.15 cases/1,000 live births (in 2003) to 0.34 cases/1,000 live births (in 2013). Rates of late-onset disease (>7 to 90 days) also rose, from 0.15 cases/1,000 live births (in 2003) to 0.39 cases/1,000 live births (in 2013). Alberta also experienced an increase in CPS IV isolates, from 2 cases (in 2003) to 24 cases (in 2013), of which the majority were hvgA negative (93.4%) [corrected]. The predominant sequence type (ST) in 2013 was ST459. Erythromycin resistance rose from 23.6% to 43.9% (in 2013). Clindamycin resistance also increased, from 12.2% to 32.5%. In summary, Alberta, Canada, has experienced an increase in GBS disease; the increase includes both neonatal and adult disease. CPS IV cases also notably increased during the surveillance period, as did resistance to erythromycin and clindamycin.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Gherardi G, Imperi M, Baldassarri L, Pataracchia M, Alfarone G, Recchia S, Orefici G, Dicuonzo G, Creti R. 2007. Molecular epidemiology and distribution of serotypes, surface proteins, and antibiotic resistance among group B streptococci in Italy. J Clin Microbiol 45:2909–2916. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00999-07. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baker CJ, Barrett FF. 1974. Group B streptococcal infections in infants: the importance of the various serotypes. JAMA 230:1158–1160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical