Integrin-linked kinase overexpression promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition via nuclear factor-κB signaling in colorectal cancer cells
- PMID: 27099440
- PMCID: PMC4823247
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i15.3969
Integrin-linked kinase overexpression promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition via nuclear factor-κB signaling in colorectal cancer cells
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effect of integrin-linked kinase (ILK) on proliferation, metastasis, and invasion of the colorectal cancer cell line SW480.
Methods: In this study, the colorectal cancer cell line SW480 was stably transfected with ILK plasmids, and small interfering RNA (siRNA) was used to knockdown expression of nuclear factor (NF)-κB/p65. Methylthiazole tetrazolium (MTT) assay was performed to measure proliferation, and the wound healing migration assay and matrigel invasion assay were used to test the metastasis and invasion ability of SW480 cells. To explore the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process, embryonic development, and the invasion and metastasis of tumors, the protein level of E-cadherin, vimentin, snail, and slug was detected by western blot. Immunofluorescence was also used to detect E-cadherin expression. Western blot was used to determine the level of phosphorylated-inhibitor of kappa B (IκB)a, inhibitor of gamma B (IγB)a, and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) expressions and to explore the ILK signaling pathway.
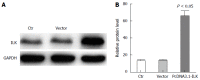
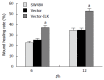
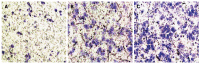
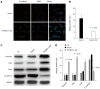
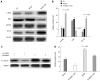
Results: Western blot results revealed that ILK expression significantly increased when ILK was overexpressed in SW480 cells (P < 0.05). Proliferation, metastasis, and invasion ability were improved in the vector-ILK group compared to the vector group (P < 0.05). Immunofluorescence results revealed that E-cadherin fluorescence intensity decreased after ILK was overexpressed (P < 0.05). Western blot results revealed that the protein expression of E-cadherin was reduced, while vimentin, snail, and slug were upregulated when ILK was overexpressed in SW480 cells (P < 0.05). In order to determine the role of the NF-κB signaling pathway in ILK overexpression promoted EMT occurrence, we overexpressed ILK in SW480 cells and found that levels of NF-κB/p65 and cytoplasmic phosphorylated-IκBa were increased and that cytoplasmic IкBa levels were decreased compared to the control group (P < 0.05). Furthermore, NF-κB/p65 knockout revealed that E-cadherin was increased in the overexpressed ILK group.
Conclusion: ILK overexpression improved the proliferation, metastasis, and invasion ability of SW480 cells, and this effect may be mediated by the NF-κB signaling pathway.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; Integrin-linked kinase; Nuclear factor-κB; Overexpression.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Overexpression of integrin-linked kinase (ILK) promotes migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition via NF-κB signaling.Acta Histochem. 2014 Apr;116(3):527-33. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2013.11.001. Epub 2013 Dec 20. Acta Histochem. 2014. PMID: 24360977
-
Overexpression of integrin-linked kinase correlates with malignant phenotype in non-small cell lung cancer and promotes lung cancer cell invasion and migration via regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-related genes.Acta Histochem. 2013 Mar;115(2):128-36. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2012.05.004. Epub 2012 Jun 9. Acta Histochem. 2013. PMID: 22683084
-
KLF5 silence attenuates proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition induction in Hep-2 cells through NF-κB signaling pathway.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 May;23(9):3867-3875. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201905_17814. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31115014
-
The novel role of Yin Yang 1 in the regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in cancer via the dysregulated NF-κB/Snail/YY1/RKIP/PTEN Circuitry.Crit Rev Oncog. 2011;16(3-4):211-26. doi: 10.1615/critrevoncog.v16.i3-4.50. Crit Rev Oncog. 2011. PMID: 22248055 Review.
-
The activated NF-kappaB-Snail-RKIP circuitry in cancer regulates both the metastatic cascade and resistance to apoptosis by cytotoxic drugs.Crit Rev Immunol. 2009;29(3):241-54. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.v29.i3.40. Crit Rev Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19538137 Review.
Cited by
-
Emodin Inhibits the Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition of Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Cells via ILK/GSK-3β/Slug Signaling Pathway.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:6253280. doi: 10.1155/2016/6253280. Epub 2016 Dec 20. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 28097141 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin-Linked Kinase Is Involved In the Proliferation and Invasion of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.J Cancer. 2020 Jan 1;11(2):324-333. doi: 10.7150/jca.33737. eCollection 2020. J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31897228 Free PMC article.
-
A Potential Role for Integrin-Linked Kinase in Colorectal Cancer Growth and Progression via Regulating Senescence and Immunity.Front Genet. 2021 Jun 7;12:638558. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.638558. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34163519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emodin Reverses the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Human Endometrial Stromal Cells by Inhibiting ILK/GSK-3β Pathway.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020 Sep 10;14:3663-3672. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S262816. eCollection 2020. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020. PMID: 32982173 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin-linked kinase affects the sensitivity of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells to chemotherapy with cisplatin via the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway.Bioengineered. 2022 May;13(5):12532-12547. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2076497. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35587162 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li J, Zhang H, Wu J, Guan H, Yuan J, Huang Z, Li M. Prognostic significance of integrin-linked kinase1 overexpression in astrocytoma. Int J Cancer. 2010;126:1436–1444. - PubMed
-
- Li J, Yang ZL, Ren X, Zou Q, Yuan Y, Liang L, Chen M, Chen S. ILK and PRDX1 are prognostic markers in squamous cell/adenosquamous carcinomas and adenocarcinoma of gallbladder. Tumour Biol. 2013;34:359–368. - PubMed
-
- Chen D, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Li J, Han B, Liu S, Wang L, Ling Y, Mao S, Wang X. Overexpression of integrin-linked kinase correlates with malignant phenotype in non-small cell lung cancer and promotes lung cancer cell invasion and migration via regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-related genes. Acta Histochem. 2013;115:128–136. - PubMed
-
- Zhao D, Tang XF, Yang K, Liu JY, Ma XR. Over-expression of integrin-linked kinase correlates with aberrant expression of Snail, E-cadherin and N-cadherin in oral squamous cell carcinoma: implications in tumor progression and metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2012;29:957–969. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

