Intestinal histoplasmosis in immunocompetent adults
- PMID: 27099446
- PMCID: PMC4823253
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i15.4027
Intestinal histoplasmosis in immunocompetent adults
Abstract
Aim: To present a retrospective analysis of clinical and endoscopic features of 4 cases of immunocompetent hosts with intestinal histoplasmosis (IH).
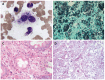
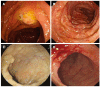
Methods: Four immunocompetent adults were diagnosed with IH between October 2005 and March 2015 at West China Hospital of Sichuan University. Clinical and endoscopic characteristics were summarized and analyzed retrospectively. GMS (Gomori methenamine silver), PAS (periodic acid-Schiff) and Giemsa staining technique were used to confirm Histoplasma capsulatum(H. capsulatum). The symptoms, signs, endoscopic presentations, radiographic imaging, pathological stain results and follow-up are presented as tables and illustrations.
Results: The cases were male patients, ranging from 33 to 61 years old, and primarily presented with non-specific symptoms such as irregular fever, weight loss, abdominal pain and distention. Hepatosplenomegaly and lymphadenopathy were the most common signs. Endoscopic manifestations were localized or diffuse congestion, edema, ulcers, and polypoid nodules with central erosion involving the terminal ileum, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon and rectum, similar to intestinal tuberculosis, tumor, and inflammatory bowel disease. Numerous yeast-like pathogens testing positive for PAS and GMS stains but negative for Giemsa were detected in the cytoplasm of the histiocytes, which were highly suggestive of H. capsulatum.
Conclusion: Immunocompetent individuals suffering from histoplasmosis are rarely reported. It is necessary that gastroenterologists and endoscopists consider histoplasmosis as a differential diagnosis, even in immunocompetent patients.
Keywords: Differential diagnosis; Disseminated histoplasmosis; Endoscopic characteristics; Immunocompetence; Intestinal histoplasmosis.
Figures
References
-
- Suh KN, Anekthananon T, Mariuz PR. Gastrointestinal histoplasmosis in patients with AIDS: case report and review. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32:483–491. - PubMed
-
- Wheat LJ, Connolly-Stringfield PA, Baker RL, Curfman MF, Eads ME, Israel KS, Norris SA, Webb DH, Zeckel ML. Disseminated histoplasmosis in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome: clinical findings, diagnosis and treatment, and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 1990;69:361–374. - PubMed
-
- Assi M, McKinsey DS, Driks MR, O’Connor MC, Bonacini M, Graham B, Manian F. Gastrointestinal histoplasmosis in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: report of 18 cases and literature review. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2006;55:195–201. - PubMed
-
- Rodriguez-Waitkus PM, Bayat V, George E, Sule N. Gastrointestinal histoplasmosis in a hepatitis C-infected individual. Mycopathologia. 2013;176:161–164. - PubMed
-
- Jain S, Koirala J, Castro-Pavia F. Isolated gastrointestinal histoplasmosis: case report and review of the literature. South Med J. 2004;97:172–174. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

