Epiretinal membrane: optical coherence tomography-based diagnosis and classification
- PMID: 27099458
- PMCID: PMC4820189
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S97722
Epiretinal membrane: optical coherence tomography-based diagnosis and classification
Abstract
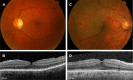
Epiretinal membrane (ERM) is a disorder of the vitreomacular interface characterized by symptoms of decreased visual acuity and metamorphopsia. The diagnosis and classification of ERM has traditionally been based on clinical examination findings. However, modern optical coherence tomography (OCT) has proven to be more sensitive than clinical examination for the diagnosis of ERM. Furthermore, OCT-derived findings, such as central foveal thickness and inner segment ellipsoid band integrity, have shown clinical relevance in the setting of ERM. To date, no OCT-based ERM classification scheme has been widely accepted for use in clinical practice and investigation. Herein, we review the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and classification of ERMs and propose an OCT-based ERM classification system.
Keywords: cellophane macular reflex; central foveal thickness; inner segment ellipsoid band; macular pucker; optical coherence tomography; preretinal macular fibrosis.
Figures
References
-
- Aung KZ, Makeyeva G, Adams MK, et al. The prevalence and risk factors of epiretinal membranes: the Melbourne Collaborative Cohort Study. Retina. 2013;33(5):1026–1034. - PubMed
-
- You Q, Xu L, Jonas JB. Prevalence and associations of epiretinal membranes in adult Chinese: the Beijing eye study. Eye (Lond) 2008;22(7):874–879. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

