Twist2 promotes kidney cancer cell proliferation and invasion by regulating ITGA6 and CD44 expression in the ECM-receptor interaction pathway
- PMID: 27099513
- PMCID: PMC4821395
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S96535
Twist2 promotes kidney cancer cell proliferation and invasion by regulating ITGA6 and CD44 expression in the ECM-receptor interaction pathway
Abstract
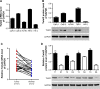
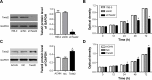
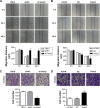
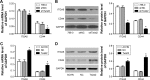
Twist2 is a member of the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) family and plays a critical role in tumorigenesis. Growing evidence has proven that Twist2 is involved in tumor progression; however, the role of Twist2 in human kidney cancer and its underlying mechanisms remain unclear. Real-time polymerase chain reaction and Western blot analysis were used to detect the expression of Twist2 in kidney cancer cells and tissues. Cell proliferation, cell cycle, apoptosis, migration, and invasion assay were analyzed using the Cell Count Kit-8, flow cytometry, wound healing, and Transwell analysis, respectively. In this study, we showed that Twist2 was upregulated in human kidney cancer tissues compared with normal kidney tissues. Twist2 promoted cell proliferation, inhibited cell apoptosis, and augmented cell migration and invasion in human kidney-cancer-derived cells in vitro. Twist2 also promoted tumor growth in vivo. Moreover, we found that the knockdown of Twist2 decreased the levels of ITGA6 and CD44 expression. This result indicates that Twist2 may promote migration and invasion of kidney cancer cells by regulating ITGA6 and CD44 expression. Therefore, our data demonstrated that Twist2 is involved in kidney cancer progression. The identification of the role of Twist2 in the migration and invasion of kidney cancer provides a potential appropriate treatment for human kidney cancer.
Keywords: CD44; ITGA6; Twist2; kidney cancer.
Figures


Similar articles
-
RETRACTED: Twist2 promotes kidney cancer cell proliferation and invasion via regulating ITGA6 and CD44 expression in the ECM-Receptor-Interaction pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2016 Jul;81:453-459. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.02.042. Epub 2016 Apr 29. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27261625 Retracted.
-
Twist2 promotes self-renewal of liver cancer stem-like cells by regulating CD24.Carcinogenesis. 2014 Mar;35(3):537-45. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgt364. Epub 2013 Nov 5. Carcinogenesis. 2014. PMID: 24193512
-
ELK3 promotes the migration and invasion of liver cancer stem cells by targeting HIF-1α.Oncol Rep. 2017 Feb;37(2):813-822. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.5293. Epub 2016 Dec 7. Oncol Rep. 2017. PMID: 27959451
-
MiR-127-3p inhibits cell growth and invasiveness by targeting ITGA6 in human osteosarcoma.IUBMB Life. 2018 May;70(5):411-419. doi: 10.1002/iub.1710. Epub 2018 Mar 23. IUBMB Life. 2018. PMID: 29573114
-
Twist1: A Double-Edged Sword in Kidney Diseases.Kidney Dis (Basel). 2020 Jul;6(4):247-257. doi: 10.1159/000505188. Epub 2020 Jan 17. Kidney Dis (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32903940 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Screening and identification of potential target genes in head and neck cancer using bioinformatics analysis.Oncol Lett. 2019 Sep;18(3):2955-2966. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10616. Epub 2019 Jul 15. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31452775 Free PMC article.
-
High-Throughput MicroRNA Profiling of Vitreoretinal Lymphoma: Vitreous and Serum MicroRNA Profiles Distinct from Uveitis.J Clin Med. 2020 Jun 12;9(6):1844. doi: 10.3390/jcm9061844. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32545709 Free PMC article.
-
Promising novel biomarkers and candidate small-molecule drugs for lung adenocarcinoma: Evidence from bioinformatics analysis of high-throughput data.Open Med (Wars). 2021 Dec 21;17(1):96-112. doi: 10.1515/med-2021-0375. eCollection 2022. Open Med (Wars). 2021. PMID: 35028418 Free PMC article.
-
Cadherin dysregulation in gastric cancer: insights into gene expression, pathways, and prognosis.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2023 Oct 31;14(5):2064-2082. doi: 10.21037/jgo-23-700. Epub 2023 Oct 26. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37969819 Free PMC article.
-
Role of anoikis-related gene PLK1 in kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma: a bioinformatics analysis and preliminary verification on promoting proliferation and migration.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jun 29;14:1211675. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1211675. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37456749 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Kim HJ, Shen SS, Ayala AG, et al. Virtual-karyotyping with SNP microarrays in morphologically challenging renal cell neoplasms: a practical and useful diagnostic modality. Am J Surg Pathol. 2009;33:1276–1286. - PubMed
-
- Harada K, Miyake H, Kusuda Y, Fujisawa M. Expression of epithelial–mesenchymal transition markers in renal cell carcinoma: impact on prognostic outcomes in patients undergoing radical nephrectomy. BJU Int. 2012;110:E1131–E1137. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

