Hormetic Effect of H2O2 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Involvement of TOR and Glutathione Reductase
- PMID: 27099601
- PMCID: PMC4822199
- DOI: 10.1177/1559325816636130
Hormetic Effect of H2O2 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Involvement of TOR and Glutathione Reductase
Abstract
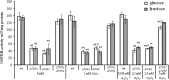
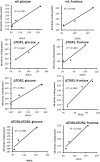
In this study, we investigated the relationship between target of rapamycin (TOR) and H2O2-induced hormetic response in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae grown on glucose or fructose. In general, our data suggest that: (1) hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) induces hormesis in a TOR-dependent manner; (2) the H2O2-induced hormetic dose-response in yeast depends on the type of carbohydrate in growth medium; (3) the concentration-dependent effect of H2O2 on yeast colony growth positively correlates with the activity of glutathione reductase that suggests the enzyme involvement in the H2O2-induced hormetic response; and (4) both TOR1 and TOR2 are involved in the reciprocal regulation of the activity of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and glyoxalase 1.
Keywords: Saccharomyces cerevisiae; TOR1; TOR2; glutathione reductase; hormesis; hydrogen peroxide; monosaccharides.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Reactive Carbonyls Induce TOR- and Carbohydrate-Dependent Hormetic Response in Yeast.ScientificWorldJournal. 2020 Mar 12;2020:4275194. doi: 10.1155/2020/4275194. eCollection 2020. ScientificWorldJournal. 2020. PMID: 32231465 Free PMC article.
-
Carbon Sources for Yeast Growth as a Precondition of Hydrogen Peroxide Induced Hormetic Phenotype.Int J Microbiol. 2015;2015:697813. doi: 10.1155/2015/697813. Epub 2015 Dec 30. Int J Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26843865 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian RAFT1 kinase domain provides rapamycin-sensitive TOR function in yeast.Genes Dev. 1996 Feb 1;10(3):279-88. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.3.279. Genes Dev. 1996. PMID: 8595879
-
TOR signaling in fission yeast.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2008 Jul-Aug;43(4):277-83. doi: 10.1080/10409230802254911. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18756382 Review.
-
Insight into Tor2, a budding yeast microdomain protein.Eur J Cell Biol. 2014 Mar;93(3):87-97. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2014.01.004. Epub 2014 Feb 14. Eur J Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24629393 Review.
Cited by
-
Hypoxia-reoxygenation Extends the Lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans via SKN-1- and DAF-16A-Dependent Stress Hormesis.Curr Aging Sci. 2025;18(2):163-173. doi: 10.2174/0118746098292667240914024812. Curr Aging Sci. 2025. PMID: 39354761
-
Reactive Carbonyls Induce TOR- and Carbohydrate-Dependent Hormetic Response in Yeast.ScientificWorldJournal. 2020 Mar 12;2020:4275194. doi: 10.1155/2020/4275194. eCollection 2020. ScientificWorldJournal. 2020. PMID: 32231465 Free PMC article.
-
Outdoor disinfectant sprays for the prevention of COVID-19: Are they safe for the environment?Sci Total Environ. 2021 Mar 10;759:144289. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144289. Epub 2020 Dec 9. Sci Total Environ. 2021. PMID: 33321443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Switching of Redox Signaling by Prdx6 Expression Decides Cellular Fate by Hormetic Phenomena Involving Nrf2 and Reactive Oxygen Species.Cells. 2022 Apr 8;11(8):1266. doi: 10.3390/cells11081266. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35455944 Free PMC article.
-
Disinfectant-induced hormesis: An unknown environmental threat of the application of disinfectants to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection during the COVID-19 pandemic?Environ Pollut. 2022 Jan 1;292(Pt B):118429. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118429. Epub 2021 Oct 29. Environ Pollut. 2022. PMID: 34743965 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Calabrese EJ. Toxicology rewrites its history and rethinks its future: giving equal focus to both harmful and beneficial effects. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2011;30(12):2658–2673. - PubMed
-
- Calabrese V, Cornelius C, Cuzzocrea S, Iavicoli I, Rizzarelli E, Calabrese EJ. Hormesis, cellular stress response and vitagenes as critical determinants in aging and longevity. Mol Aspects Med. 2011;32(4-6):279–304. - PubMed
-
- Lushchak VI. Free radicals, reactive oxygen species, oxidative stress and its classification. Chem Biol Interact. 2014;224c:164–175. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

