Polyhydramnios and cerebellar atrophy: a prenatal presentation of mitochondrial encephalomyopathy caused by mutations in the FBXL4 gene
- PMID: 27099744
- PMCID: PMC4831400
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.511
Polyhydramnios and cerebellar atrophy: a prenatal presentation of mitochondrial encephalomyopathy caused by mutations in the FBXL4 gene
Abstract
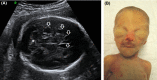
Severe recessive mitochondrial myopathy caused by FBXL4 gene mutations may present prenatally with polyhydramnios and cerebellar hypoplasia. Characteristic dysmorphic features are: high and arched eyebrows, triangular face, a slight upslant of palpebral fissures, and a prominent pointed chin. Metabolic investigations invariably show increased serum lactate and pyruvate levels.
Keywords: Cerebellar atrophy; FBXL4 gene; encephalomyopathy; lactate; mitochondrial encephalopathy; polyhydramnios; pyruvate.
Figures
References
-
- Harman, C. 2008. Amniotic fluid abnormalities. Semin. Perinatol. 32:288–294. - PubMed
-
- Dashe, J. , McIntire D., Ramus R., Santos‐Ramos R., and Twickler D. M.. 2002. Hydramnios: anomaly prevalence and sonographic detection. Obstet. Gynecol. 100:134–139. - PubMed
-
- Raju, G. P. , Li H.‐C., Bali D., Chen Y. T., Urion D. K., Lidov H. G., et al. 2008. A case of congenital glycogen storage disease type IV with a novel GBE1 mutation. J. Child Neurol. 23:349–352. - PubMed
-
- Magann, E. , Chauhan S., Doherty D., Lutgendorf M. A., Magann M. I., Morrison J. C., et al. 2007. A review of idiopathic hydramnios and pregnancy outcomes. Obstet. Gynecol. Surv. 62:795–802. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

