Evolution of Costs of Inflammatory Bowel Disease over Two Years of Follow-Up
- PMID: 27099937
- PMCID: PMC4839678
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142481
Evolution of Costs of Inflammatory Bowel Disease over Two Years of Follow-Up
Abstract
Background: With the increasing use of anti-TNF therapy in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), a shift of costs has been observed with medication costs replacing hospitalization and surgery as major cost driver. We aimed to explore the evolution of IBD-related costs over two years of follow-up.
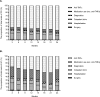
Methods and findings: In total 1,307 Crohn's disease (CD) patients and 915 ulcerative colitis (UC) patients were prospectively followed for two years by three-monthly web-based questionnaires. Changes of healthcare costs, productivity costs and out-of-pocket costs over time were assessed using mixed model analysis. Multivariable logistic regression analysis was used to identify costs drivers. In total 737 CD patients and 566 UC were included. Total costs were stable over two years of follow-up, with annual total costs of €7,835 in CD and €3,600 in UC. However, within healthcare costs, the proportion of anti-TNF therapy-related costs increased from 64% to 72% in CD (p<0.01) and from 31% to 39% in UC (p < 0.01). In contrast, the proportion of hospitalization costs decreased from 19% to 13% in CD (p<0.01), and 22% to 15% in UC (p < 0.01). Penetrating disease course predicted an increase of healthcare costs (adjusted odds ratio (adj. OR) 1.95 (95% CI 1.02-3.37) in CD and age <40 years in UC (adj. OR 4.72 (95% CI 1.61-13.86)).
Conclusions: BD-related costs remained stable over two years. However, the proportion of anti-TNF-related healthcare costs increased, while hospitalization costs decreased. Factors associated with increased costs were penetrating disease course in CD and age <40 in UC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- van der Valk ME, Mangen MJ, Leenders M, Dijkstra G, van Bodegraven AA, Fidder HH, et al. Healthcare costs of inflammatory bowel disease have shifted from hospitalisation and surgery towards anti-TNF alpha therapy: results from the COIN study. Gut 2014;63:72–9. 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-303376 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stark R, Konig HH, Leidl R. Costs of inflammatory bowel disease in Germany. Pharmacoeconomics 2006;24:797–814. - PubMed
-
- Odes S, Vardi H, Friger M, Russel MG, Munkholm P, Politi P, et al. Cost analysis and cost determinants in a European inflammatory bowel disease inception cohort with 10 years of follow-up evaluation. Gastroenterology 2006;131:719–728. - PubMed
-
- Juan J, Estiarte R, Colomé E, Artés M, Jiménez FJ, Alonso J. Burden of illness of Crohn's disease in Spain. Dig Liver Dis 2003;35:853–861. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

