Non-Heme Iron Absorption and Utilization from Typical Whole Chinese Diets in Young Chinese Urban Men Measured by a Double-Labeled Stable Isotope Technique
- PMID: 27099954
- PMCID: PMC4839665
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153885
Non-Heme Iron Absorption and Utilization from Typical Whole Chinese Diets in Young Chinese Urban Men Measured by a Double-Labeled Stable Isotope Technique
Abstract
Background: This study was to observe the non-heme iron absorption and biological utilization from typical whole Chinese diets in young Chinese healthy urban men, and to observe if the iron absorption and utilization could be affected by the staple food patterns of Southern and Northern China.
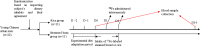
Materials and methods: Twenty-two young urban men aged 18-24 years were recruited and randomly assigned to two groups in which the staple food was rice and steamed buns, respectively. Each subject received 3 meals containing approximately 3.25 mg stable 57FeSO4 (the ratio of 57Fe content in breakfast, lunch and dinner was 1:2:2) daily for 2 consecutive days. In addition, approximately 2.4 mg 58FeSO4 was administered intravenously to each subject at 30-60 min after dinner each day. Blood samples were collected from each subject to measure the enrichment of the 57Fe and 58Fe. Fourteen days after the experimental diet, non-heme iron absorption was assessed by measuring 57Fe incorporation into red blood cells, and absorbed iron utilization was determined according to the red blood cell incorporation of intravenously infused 58Fe SO4.
Results: Non-heme iron intake values overall, and in the rice and steamed buns groups were 12.8 ±2.1, 11.3±1.3 and 14.3±1.5 mg, respectively; the mean 57Fe absorption rates were 11±7%, 13±7%, and 8±4%, respectively; and the mean infused 58Fe utilization rates were 85±8%, 84±6%, and 85±10%, respectively. There was no significantly difference in the iron intakes, and 57Fe absorption and infused 58Fe utilization rates between rice and steamed buns groups (all P>0.05).
Conclusion: We present the non-heme iron absorption and utilization rates from typical whole Chinese diets among young Chinese healthy urban men, which was not affected by the representative staple food patterns of Southern and Northern China. This study will provide a basis for the setting of Chinese iron DRIs.
Conflict of interest statement
Similar articles
-
Bioavailability and incorporation of nonheme iron from a representative Chinese diet in young urban Chinese women.Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2019;28(2):214-222. doi: 10.6133/apjcn.201906_28(2).0002. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2019. PMID: 31192549 Clinical Trial.
-
Determination of iron absorption using erythrocyte iron incorporation of two stable isotopes of iron (57Fe and 58Fe) in very low birthweight premature infants.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1995 Aug;21(2):190-9. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199508000-00011. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1995. PMID: 7472906
-
A double stable isotope technique for measuring iron absorption in infants.Br J Nutr. 1994 Mar;71(3):411-24. doi: 10.1079/bjn19940148. Br J Nutr. 1994. PMID: 8172870 Clinical Trial.
-
Iron requirements and bioavailability of dietary iron.Experientia Suppl. 1983;44:223-44. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-6540-1_13. Experientia Suppl. 1983. PMID: 6315480 Review.
-
Clinical measurements of iron absorption.Clin Haematol. 1977 Oct;6(3):567-81. Clin Haematol. 1977. PMID: 334423 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Differences in nonheme iron absorption between healthy adults of East Asian or Northern European ancestry from the Iron Genes in East Asian and Northern European Adults Study (FeGenes): A cross-sectional stable iron isotope study.Am J Clin Nutr. 2025 Feb;121(2):417-426. doi: 10.1016/j.ajcnut.2024.11.015. Am J Clin Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39909711
-
[Erchen Decoction improves iron homeostasis in mice with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by regulating iron transport capacity in the spleen].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2023 Aug 20;43(8):1287-1296. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2023.08.04. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2023. PMID: 37712264 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Iron physiological requirements in Chinese adults assessed by the stable isotope labeling technique.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2018 Apr 20;15:29. doi: 10.1186/s12986-018-0262-2. eCollection 2018. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2018. PMID: 29721032 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological requirements for iron in women of reproductive age assessed by the stable isotope tracer technique.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2019 Aug 19;16:55. doi: 10.1186/s12986-019-0384-1. eCollection 2019. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2019. PMID: 31452667 Free PMC article.
References
-
- U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (April 2012 [cited 2013 Feb 4]). Second national report on biochemical indicators of diet and nutrition in the U.S. population 2012. Atlanta (GA): National Center for Environmental Health. Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/nutritionreport.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical