Implication of sphingosin-1-phosphate in cardiovascular regulation
- PMID: 27100508
- PMCID: PMC4865951
- DOI: 10.2741/4458
Implication of sphingosin-1-phosphate in cardiovascular regulation
Abstract
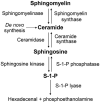
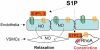
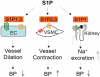
Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) is a bioactive sphingolipid metabolite generated by phosphorylation of sphingosine catalyzed by sphingosine kinase. S1P acts mainly through its high affinity G-protein-coupled receptors and participates in the regulation of multiple systems, including cardiovascular system. It has been shown that S1P signaling is involved in the regulation of cardiac chronotropy and inotropy and contributes to cardioprotection as well as cardiac remodeling; S1P signaling regulates vascular function, such as vascular tone and endothelial barrier, and possesses an anti-atherosclerotic effect; S1P signaling is also implicated in the regulation of blood pressure. Therefore, manipulation of S1P signaling may offer novel therapeutic approaches to cardiovascular diseases. As several S1P receptor modulators and sphingosine kinase inhibitors have been approved or under clinical trials for the treatment of other diseases, it may expedite the test and implementation of these S1P-based drugs in cardiovascular diseases.
Figures


References
-
- Ghosh TK, Bian J, Gill DL. Intracellular calcium release mediated by sphingosine derivatives generated in cells. Science. 1990;248(4963):1653–6. DOI: 10.1126/science.2163543. - PubMed
-
- Liu X, Zhang QH, Yi GH. Regulation of metabolism and transport of sphingosine-1-phosphate in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012;363(1-2):21–33. DOI: 10.1007/s11010-011-1154-1. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

