Alarmins and Antitumor Immunity
- PMID: 27101817
- PMCID: PMC6314656
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2016.03.021
Alarmins and Antitumor Immunity
Abstract
Purpose: Alarmins are constitutively present endogenous molecules that essentially act as early warning signals for the immune system. We provide a brief overview of major alarmins and highlight their roles in tumor immunity.
Methods: We searched PubMed up to January 10, 2016, using alarmins and/or damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), as key words. We selected and reviewed articles that focused on the discovery and functions of alarmin and their roles in tumor immunity.
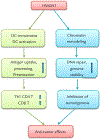
Findings: Alarmins are essentially endogenous immunostimulatory DAMP molecules that are exposed in response to danger (eg, infection or tissue injury) as a result of degranulation, cell death, or induction. They are sensed by chemotactic receptors and pattern recognition receptors to induce immune responses by promoting the recruitment and activation of leukocytes, particularly antigen-presenting cells.
Implications: Accumulating data suggest that certain alarmins, High-mobility group nucleosome-binding protein 1 (HMGN1) in particular, contribute to the generation of antitumor immunity. Some alarmins can also be used as cancer biomarkers. Therefore, alarmins can potentially be applied for our fight against cancers.
Keywords: alarmin; biomarker; damage-associated molecular patterns; immune response; pattern recognition receptor; tumor immunity.
Copyright © 2016. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors have indicated that they have no conflicts of interest regarding the content of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Janeway CA Jr. The immune system evolved to discriminate infectious nonself from noninfectious self. Immunol Today. 1992;13:11–16. - PubMed
-
- Tolerance Matzinger P., danger, and the extended family. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:991–1045. - PubMed
-
- Gallucci S, Matzinger P. Danger signals: SOS to the immune system. Curr Opin Immunol. 2001;13:114–119. - PubMed
-
- Wang H, et al. HMGB1 as a late mediator of lethal systemic inflammation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001; 164:1768–1773. - PubMed
-
- Czura CJ, Wang H, Tracey KJ. Dual roles for HMGB1: DNA binding and cytokine. J Endotoxin Res. 2001;7:315–321. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

