Wogonoside prevents colitis-associated colorectal carcinogenesis and colon cancer progression in inflammation-related microenvironment via inhibiting NF-κB activation through PI3K/Akt pathway
- PMID: 27102438
- PMCID: PMC5085157
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.8815
Wogonoside prevents colitis-associated colorectal carcinogenesis and colon cancer progression in inflammation-related microenvironment via inhibiting NF-κB activation through PI3K/Akt pathway
Abstract
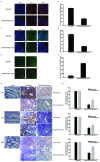
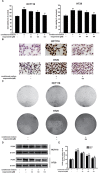
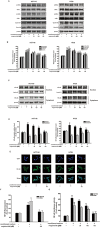
The inflammatory microenvironment has been reported to be correlated with tumor initiation and malignant development. In the previous studies we have found that wogonoside exerts anti-neoplastic and anti-inflammatory activities. In this study, we aimed to further investigate the chemopreventive effects of wogonoside on colitis-associated cancer and delineated the potential mechanisms. In the azoxymethane initiated and dextran sulfate sodium (AOM/DSS) promoted colorectal carcinogenesis mouse model, wogonoside significantly reduced the disease severity, lowered tumor incidence and inhibited the development of colorectal adenomas. Moreover, wogonoside inhibited inflammatory cells infiltration and cancer cell proliferation at tumor site. Furthermore, wogonoside dramatically decreased the secretion and expression of IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α as well as the nuclear expression of NF-κB in adenomas and surrounding tissues. In vitro results showed that wogonoside suppressed the proliferation of human colon cancer cells in the inflammatory microenvironment. Mechanistically, we found that wogonoside inhibited NF-κB activation via PI3K/Akt pathway. In conclusion, our results demonstrated that wogonoside attenuated colitis-associated tumorigenesis in mice and inhibited the progression of human colon cancer in inflammation-related microenvironment via suppressing NF-κB activation by PI3K/Akt pathway, indicating that wogonoside could be a promising therapeutic agent for colorectal cancer.
Keywords: AOM/DSS mouse model; NF-κB; colitis-associated cancer; wogonoside.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Murray T, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 2008;58:71–96. - PubMed
-
- Danese S, Mantovani A. Inflammatory bowel disease and intestinal cancer: a paradigm of the Yin-Yang interplay between inflammation and cancer. Oncogene. 2010;29:3313–3323. - PubMed
-
- Vakkila J, Lotze MT. Inflammation and necrosis promote tumour growth. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:641–648. - PubMed
-
- Balkwill F, Mantovani A. Inflammation and cancer: back to Virchow? Lancet. 2001;357:539–545. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

