Effects of low dose estrogen therapy on the vaginal microbiomes of women with atrophic vaginitis
- PMID: 27103314
- PMCID: PMC4840317
- DOI: 10.1038/srep24380
Effects of low dose estrogen therapy on the vaginal microbiomes of women with atrophic vaginitis
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Effects of low dose estrogen therapy on the vaginal microbiomes of women with atrophic vaginitis.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 29;6:34119. doi: 10.1038/srep34119. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27897166 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
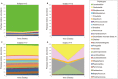
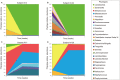
Atrophic vaginitis (AV) is common in postmenopausal women, but its causes are not well understood. The symptoms, which include vaginal itching, burning, dryness, irritation, and dyspareunia, can usually be alleviated by low doses of estrogen given orally or locally. Regrettably, the composition of vaginal bacterial communities in women with AV have not been fully characterized and little is known as to how these communities change over time in response to hormonal therapy. In the present intervention study we determined the response of vaginal bacterial communities in postmenopausal women with AV to low-dose estrogen therapy. The changes in community composition in response to hormonal therapy were rapid and typified by significant increases in the relative abundance of Lactobacillus spp. that were mirrored by a decreased relative abundance of Gardnerella. These changes were paralleled by a significant four-fold increase in serum estradiol levels and decreased vaginal pH, as well as nearly a two-fold increase in the Vaginal Maturation Index (VMI). The results suggest that after menopause a vaginal microbiota dominated by species of Lactobacillus may have a beneficial role in the maintenance of health and these findings that could lead to new strategies to protect postmenopausal women from AV.
Figures



References
-
- Sturdee D. W. & Panay N. International Menopause Society Writing Group. Recommendations for the management of postmenopausal vaginal atrophy. Climacteric 13, 509–522 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Castelo-Branco C., Cancelo M. J., Villero J., Nohales F. & Juliá M. D. Management of post-menopausal vaginal atrophy and atrophic vaginitis. Maturitas 52S, S46–S52 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Skouby S. O. et al. Climacteric medicine: European Menopause and Andropause Society (EMAS) 2004/2005 position statements on peri- and postmenopausal hormone replacement therapy. Maturitas 51, 8–14 (2005). - PubMed
-
- The North American Menopause Society. Management of symptomatic vulvovaginal atrophy: 2013 position statement of The North American Menopause Society. Menopause. 20, 888–902 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Simon J. A., Reape K. Z., Wininger S. & Hait H. Randomized, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of synthetic conjugated estrogens B for the treatment of vulvovaginal atrophy in healthy postmenopausal women. Fertil. Steril. 90, 1132–1138 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

