Clinical Pattern of Early-Onset Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Saudi Arabia: A Multicenter National Study
- PMID: 27104817
- PMCID: PMC4949013
- DOI: 10.1097/MIB.0000000000000796
Clinical Pattern of Early-Onset Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Saudi Arabia: A Multicenter National Study
Abstract
Background: The objectives of this multicenter national study were to compare the clinical phenotype of early-onset inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) (EO-IBD) with IBD in older children and to examine whether there is any variability in consanguinity rate and familial aggregation in EO-IBD compared with later onset IBD.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was performed on children aged 0 to 14 years with IBD in 17 centers located in geographically distinct regions in Saudi Arabia, from 2003 to 2012. Data of patients with EO-IBD (0 to <6 yrs) were compared with those with later onset IBD (6-14 yrs). Moreover, we evaluated differences in clinical pattern of infantile or toddler onset IBD subgroup (0-3 yr) as compared with those presenting in older children.
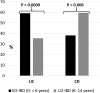
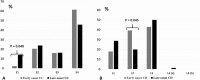
Results: Of 352 IBD patients identified during the 10-year study period, 76 children (21.6%) younger than 6 years were diagnosed with IBD. Among the Crohn's disease (CD) group, infantile or toddler onset CD subgroup showed a more frequent isolated colonic involvement (L2) than later-onset group (57% versus 20%; P = 0.002). Positive family history was significantly more common in the infantile or toddler onset ulcerative colitis subgroup (29.4% versus 4.2% in later onset ulcerative colitis; P < 0.0001). The consanguinity rate was significantly higher in the infantile or toddler onset CD subgroup as compared with later onset CD group (57.1% versus 25.3%; P = 0.04).
Conclusions: In conclusion, EO-IBD exhibits a unique clinical phenotype with a strikingly higher familial aggregation in early-onset ulcerative colitis. Our data suggest a significant genetic impact on the onset of CD in the very young children.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Aloi M, Lionetti P, Barabino A, et al. Phenotype and disease course of early-onset pediatric inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2014;20:597–605. - PubMed
-
- Aloi M, D'Arcangelo G, Pofi F, et al. Presenting features and disease course of pediatric ulcerative colitis. J Crohn's Colitis. 2013;7:e509–e515. - PubMed
-
- Paul T, Birnbaum A, Pal DK, et al. Distinct phenotype of early childhood inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2006;40:583–586. - PubMed
-
- Heyman MB, Kirschner BS, Gold BD, et al. Children with early-onset inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): analysis of a pediatric IBD consortium registry. J Pediatr. 2005;146:35–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

