Metabolic Regulation of Gene Expression by Histone Lysine β-Hydroxybutyrylation
- PMID: 27105115
- PMCID: PMC5540445
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.03.036
Metabolic Regulation of Gene Expression by Histone Lysine β-Hydroxybutyrylation
Abstract
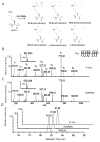
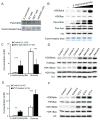
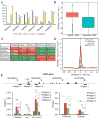
Here we report the identification and verification of a β-hydroxybutyrate-derived protein modification, lysine β-hydroxybutyrylation (Kbhb), as a new type of histone mark. Histone Kbhb marks are dramatically induced in response to elevated β-hydroxybutyrate levels in cultured cells and in livers from mice subjected to prolonged fasting or streptozotocin-induced diabetic ketoacidosis. In total, we identified 44 histone Kbhb sites, a figure comparable to the known number of histone acetylation sites. By ChIP-seq and RNA-seq analysis, we demonstrate that histone Kbhb is a mark enriched in active gene promoters and that the increased H3K9bhb levels that occur during starvation are associated with genes upregulated in starvation-responsive metabolic pathways. Histone β-hydroxybutyrylation thus represents a new epigenetic regulatory mark that couples metabolism to gene expression, offering a new avenue to study chromatin regulation and diverse functions of β-hydroxybutyrate in the context of important human pathophysiological states, including diabetes, epilepsy, and neoplasia.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- CAHILL GF. Fuel metabolism in starvation. Annual Review of Nutrition. 2006;26:1–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK089098/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM115961/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA177925/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG030593/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK071900/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK057751/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM101171/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM105933/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023166/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK034989/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK082664/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM059507/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

