MALT1 inhibitors prevent the development of DSS-induced experimental colitis in mice via inhibiting NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome activation
- PMID: 27105502
- PMCID: PMC5058699
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.8867
MALT1 inhibitors prevent the development of DSS-induced experimental colitis in mice via inhibiting NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome activation
Abstract
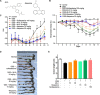
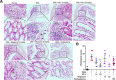
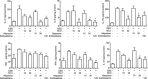
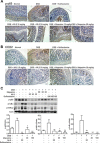
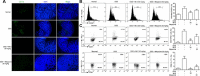
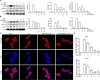
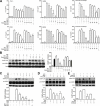
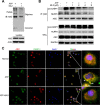
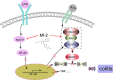
Mucosa-associated-lymphoid-tissue lymphoma-translocation gene 1 (MALT1), a paracaspase and essential regulator for nuclear factor kB (NF-κB) activation, plays an important role in innate and adaptive immunity. Suppression of MALT1 protease activity with small molecule inhibitors showed promising efficacies in subtypes of B cell lymphoma and improvement in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis model. However, whether MALT1 inhibitors could ameliorate colitis remains unclear. In the present study, we examined the pharmacological effect of two specific MALT1 inhibitors MI-2 and mepazine on the dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced experimental colitis in mice, followed by mechanistic analysis on NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Treatment with MI-2 and mepazine dose-dependently attenuated symptoms of colitis in mice, evidenced by reduction in the elevated disease activity index, the shortening of colon length as well as the histopathologic improvement. Moreover, protein and mRNA levels of DSS-induced proinflammatory cytokines in colon, including TNF, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-18, IL-17A and IFN-γ, were markedly suppressed by MALT1 inhibitors. The underlying mechanisms for the protective effect of MALT1 inhibitors in DSS-induced colitis may be attributed to its inhibition on NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages. The in vitro study showed that MALT1 inhibitors decreased production of IL-1β/IL-18 in phorbol myristate acetate-differentiated THP-1 cells and bone marrow derived macrophage via suppressing the activation of NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome. Taken together, our results demonstrated that inhibition of the protease activity of MALT1 might be a viable strategy to treat inflammatory bowel disease and the NLRP3 inflammasome and NF-κB activation are critical components in MALT1 signaling cascades in this disease model.
Keywords: IL-1β; MALT1; NF-κB; NLRP3 inflammasome; colitis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest none declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Wogonoside protects against dextran sulfate sodium-induced experimental colitis in mice by inhibiting NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome activation.Biochem Pharmacol. 2015 Mar 15;94(2):142-54. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2015.02.002. Epub 2015 Feb 10. Biochem Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25677765
-
Suppression of NF-κB signaling and NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages is responsible for the amelioration of experimental murine colitis by the natural compound fraxinellone.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014 Nov 15;281(1):146-56. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2014.10.002. Epub 2014 Oct 13. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25448682
-
A novel benzo[d]imidazole derivate prevents the development of dextran sulfate sodium-induced murine experimental colitis via inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome.Biochem Pharmacol. 2013 May 15;85(10):1504-12. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2013.03.008. Epub 2013 Mar 15. Biochem Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23506741
-
NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome axis and risk of Parkinson's disease in Type 2 diabetes mellitus: A narrative review and new perspective.J Cell Mol Med. 2023 Jul;27(13):1775-1789. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17784. Epub 2023 May 21. J Cell Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37210624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contradictory Effects of NLRP3 Inflammasome Regulatory Mechanisms in Colitis.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 30;21(21):8145. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218145. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33143375 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Restorative effects of Rg3-enriched Korean Red Ginseng and Persicaria tinctoria extract on oxazolone-induced ulcerative colitis in mice.J Ginseng Res. 2022 Sep;46(5):628-635. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2021.07.001. Epub 2021 Jul 17. J Ginseng Res. 2022. PMID: 36090686 Free PMC article.
-
A novel herbal formulation consisting of red ginseng extract and Epimedium koreanum Nakai-attenuated dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice.J Ginseng Res. 2020 Nov;44(6):833-842. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2020.02.003. Epub 2020 Mar 21. J Ginseng Res. 2020. PMID: 33192127 Free PMC article.
-
The CBM-opathies-A Rapidly Expanding Spectrum of Human Inborn Errors of Immunity Caused by Mutations in the CARD11-BCL10-MALT1 Complex.Front Immunol. 2018 Sep 19;9:2078. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02078. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30283440 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Probiotic Cocktail Alleviates Intestinal Inflammation Through Improving Gut Microbiota and Metabolites in Colitis Mice.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Jun 15;12:886061. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.886061. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35782138 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological Inhibition of MALT1 Ameliorates Autoimmune Pathogenesis and Can Be Uncoupled From Effects on Regulatory T-Cells.Front Immunol. 2022 May 9;13:875320. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.875320. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35615349 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Farrell RJ, Peppercorn MA. Ulcerative colitis. Lancet. 2002;359:331–340. - PubMed
-
- Triantafillidis JK, Nasioulas G, Kosmidis PA. Colorectal cancer and inflammatory bowel disease: epidemiology, risk factors, mechanisms of carcinogenesis and prevention strategies. Anticancer Res. 2009;29:2727–2737. - PubMed
-
- Wei J, Feng J. Signaling pathways associated with inflammatory bowel disease. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2010;4:105–117. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

