NLRX1 suppresses tumorigenesis and attenuates histiocytic sarcoma through the negative regulation of NF-κB signaling
- PMID: 27105514
- PMCID: PMC5078078
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.8861
NLRX1 suppresses tumorigenesis and attenuates histiocytic sarcoma through the negative regulation of NF-κB signaling
Abstract
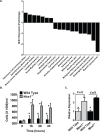
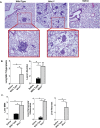
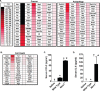
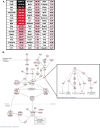
Histiocytic sarcoma is an uncommon malignancy in both humans and veterinary species. Research exploring the pathogenesis of this disease is scarce; thus, diagnostic and therapeutic options for patients are limited. Recent publications have suggested a role for the NLR, NLRX1, in acting as a tumor suppressor. Based on these prior findings, we hypothesized that NLRX1 would function to inhibit tumorigenesis and thus the development of histiocytic sarcoma. To test this, we utilized Nlrx1-/- mice and a model of urethane-induced tumorigenesis. Nlrx1-/- mice exposed to urethane developed splenic histiocytic sarcoma that was associated with significant up-regulation of the NF-κB signaling pathway. Additionally, development of these tumors was also significantly associated with the increased regulation of genes associated with AKT signaling, cell death and autophagy. Together, these data show that NLRX1 suppresses tumorigenesis and reveals new genetic pathways involved in the pathobiology of histiocytic sarcoma.
Keywords: NLR; Nod-like receptor; cancer; inflammation; urethane.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Innate Immune Receptor NLRX1 Functions as a Tumor Suppressor by Reducing Colon Tumorigenesis and Key Tumor-Promoting Signals.Cell Rep. 2016 Mar 22;14(11):2562-75. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.02.064. Epub 2016 Mar 10. Cell Rep. 2016. PMID: 26971998 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of NLRX1 Exacerbates Neural Tissue Damage and NF-κB Signaling following Brain Injury.J Immunol. 2017 Nov 15;199(10):3547-3558. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700251. Epub 2017 Oct 9. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28993512 Free PMC article.
-
NLRX1 acts as tumor suppressor by regulating TNF-α induced apoptosis and metabolism in cancer cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 May;1853(5):1073-86. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2015.01.016. Epub 2015 Jan 30. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25639646
-
NLRX1 Is a Multifaceted and Enigmatic Regulator of Immune System Function.Front Immunol. 2019 Oct 11;10:2419. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02419. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31681307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Underlying Mechanisms and Related Diseases Behind the Complex Regulatory Role of NOD-Like Receptor X1.DNA Cell Biol. 2022 May;41(5):469-478. doi: 10.1089/dna.2022.0051. Epub 2022 Mar 31. DNA Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35363060 Review.
Cited by
-
The interaction of O-GlcNAc-modified NLRX1 and IKK-α modulates IL-1β expression in M1 macrophages.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2022 May;58(5):408-418. doi: 10.1007/s11626-022-00654-1. Epub 2022 May 5. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2022. PMID: 35513753
-
Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor X1 restricts porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus-2 replication by interacting with viral Nsp9.Virus Res. 2019 Jul 15;268:18-26. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2019.05.011. Epub 2019 May 24. Virus Res. 2019. PMID: 31132368 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics analysis and experimental verification of NLRX1 as a prognostic factor for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2024 Apr 11;27(6):264. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14397. eCollection 2024 Jun. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38659420 Free PMC article.
-
NLRX1 Deficiency Alters the Gut Microbiome and Is Further Exacerbated by Adherence to a Gluten-Free Diet.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 28;13:882521. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.882521. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35572547 Free PMC article.
-
NLR in eXile: Emerging roles of NLRX1 in immunity and human disease.Immunology. 2021 Mar;162(3):268-280. doi: 10.1111/imm.13291. Epub 2020 Dec 28. Immunology. 2021. PMID: 33314068 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Laviv Y, Zagzag D, Fichman-Horn S, Michowitz S. Primary central nervous system histiocytic sarcoma. Brain tumor pathology. 2013;30:192–195. - PubMed
-
- Chatterjee S, Crozet L, Damotte D, Iribarren K, Schramm C, Alifano M, Lupo A, Cherfils-Vicini J, Goc J, Katsahian S, Younes M, Dieu-Nosjean MC, Fridman WH, Sautes-Fridman C, Cremer I. TLR7 promotes tumor progression, chemotherapy resistance, and poor clinical outcomes in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer research. 2014;74:5008–5018. - PubMed
-
- Samara KD, Antoniou KM, Karagiannis K, Margaritopoulos G, Lasithiotaki I, Koutala E, Siafakas NM. Expression profiles of Toll-like receptors in non-small cell lung cancer and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. International journal of oncology. 2012;40:1397–1404. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

