Urate Handling in the Human Body
- PMID: 27105641
- PMCID: PMC4841844
- DOI: 10.1007/s11926-016-0587-7
Urate Handling in the Human Body
Abstract
Elevated serum urate concentration is the primary cause of gout. Understanding the processes that affect serum urate concentration is important for understanding the etiology of gout and thereby understanding treatment. Urate handing in the human body is a complex system including three major processes: production, renal elimination, and intestinal elimination. A change in any one of these can affect both the steady-state serum urate concentration as well as other urate processes. The remarkable complexity underlying urate regulation and its maintenance at high levels in humans suggests that this molecule could potentially play an interesting role other than as a mere waste product to be eliminated as rapidly as possible.
Keywords: Excretion; FEUA; Gout; Urate; Uric acid.
Figures
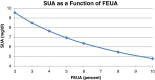

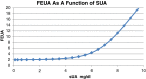
References
-
- Wang Z, Königsberger E. Solubility equilibria in the uric acid-sodium urate-water system. Thermochim Acta. 1998;310:237–42. doi: 10.1016/S0040-6031(97)00230-X. - DOI
-
- Zhang W, Doherty M, Bardin T, Pascual E, Barskova V, Conaghan P, et al. EULAR evidence based recommendations for gout, part II: management: report of a task force of the EULAR Standing Committee for International Clinical Studies Including Therapeutics (ESCISIT) Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65(10):1312–24. doi: 10.1136/ard.2006.055269. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Khanna D, Fitzgerald JD, Khanna PP, Bae S, Singh MK, Neogi T, et al. 2012 American College of Rheumatology guidelines for management of gout, part 1: systematic nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic therapeutic approaches to hyperuricemia. Arthritis Care Res. 2012;64(10):1431–46. doi: 10.1002/acr.21772. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

