An informatics research agenda to support precision medicine: seven key areas
- PMID: 27107452
- PMCID: PMC4926738
- DOI: 10.1093/jamia/ocv213
An informatics research agenda to support precision medicine: seven key areas
Abstract
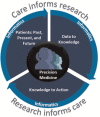
The recent announcement of the Precision Medicine Initiative by President Obama has brought precision medicine (PM) to the forefront for healthcare providers, researchers, regulators, innovators, and funders alike. As technologies continue to evolve and datasets grow in magnitude, a strong computational infrastructure will be essential to realize PM's vision of improved healthcare derived from personal data. In addition, informatics research and innovation affords a tremendous opportunity to drive the science underlying PM. The informatics community must lead the development of technologies and methodologies that will increase the discovery and application of biomedical knowledge through close collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and patients. This perspective highlights seven key areas that are in need of further informatics research and innovation to support the realization of PM.
Keywords: biomarkers; data sharing; informatics; precision medicine.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the American Medical Informatics Association.
Figures
References
-
- Califf RM, Platt R. Embedding cardiovascular research into practice. JAMA. 2013. Nov 20;310(9):2037–8. - PubMed
-
- Kulynych J, Greely H. Every patient a subject: when personalized medicine, genomic research, and privacy collide. Slate.com. 30 December 2014.
-
- Gymrek M, McGuire AL, Golan D, et al. . Identifying personal genomes by surname inference. Science. 2013;339(6117):321–324. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

