When do newborns die? A systematic review of timing of overall and cause-specific neonatal deaths in developing countries
- PMID: 27109087
- PMCID: PMC4848744
- DOI: 10.1038/jp.2016.27
When do newborns die? A systematic review of timing of overall and cause-specific neonatal deaths in developing countries
Abstract
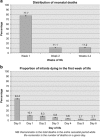
About 99% of neonatal deaths occur in low- and middle-income countries. There is a paucity of information on the exact timing of neonatal deaths in these settings. The objective of this review was to determine the timing of overall and cause-specific neonatal deaths in developing country settings. We searched MEDLINE via PubMed, Cochrane CENTRAL, WHOLIS and CABI using sensitive search strategies. Searches were limited to studies involving humans published in the last 10 years. A total of 22 studies were included in the review. Pooled results indicate that about 62% of the total neonatal deaths occurred during the first 3 days of life; the first day alone accounted for two-thirds. Almost all asphyxia-related and the majority of prematurity- and malformation-related deaths occurred in the first week of life (98%, 83% and 78%, respectively). Only one-half of sepsis-related deaths occurred in the first week while one-quarter occurred in each of the second and third to fourth weeks of life. The distribution of both overall and cause-specific mortality did not differ greatly between Asia and Africa. The first 3 days after birth account for about 30% of under-five child deaths. The first week of life accounts for most of asphyxia-, prematurity- and malformation-related mortality and one-half of sepsis-related deaths.
Figures

References
-
- Liu L, Oza S, Hogan D, Perin J, Rudan I, Lawn JE et al. Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality in 2000-13, with projections to inform post-2015 priorities: an updated systematic analysis. Lancet 2015; 385: 430–440. - PubMed
-
- Black RE, Cousens S, Johnson HL, Lawn JE, Rudan I, Bassani DG et al. Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality in 2008: a systematic analysis. Lancet 2010; 375: 1969–1987. - PubMed
-
- Lawn JE, Cousens S, Zupan J. Lancet Neonatal Survival Steering Team. 4 million neonatal deaths: when? where? why? Lancet 2005; 365: 891–900. - PubMed
-
- Lawn JE, Wilczynska-Ketende K, Cousens SN. Estimating the causes of 4 million neonatal deaths in the year 2000. Int J Epidemiol 2006; 35: 706–718. - PubMed
-
- United States Agency for International Development. List of developing countries—USAID. Available at http://www.usaid.gov/sites/default/files/documents/1876/310maa.pdf (accessed 6 May 2015).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

