Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes Afford New Opportunities in Inherited Cardiovascular Disease Modeling
- PMID: 27110425
- PMCID: PMC4826691
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/3582380
Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes Afford New Opportunities in Inherited Cardiovascular Disease Modeling
Abstract
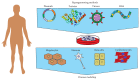
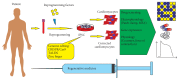
Fundamental studies of molecular and cellular mechanisms of cardiovascular disease pathogenesis are required to create more effective and safer methods of their therapy. The studies can be carried out only when model systems that fully recapitulate pathological phenotype seen in patients are used. Application of laboratory animals for cardiovascular disease modeling is limited because of physiological differences with humans. Since discovery of induced pluripotency generating induced pluripotent stem cells has become a breakthrough technology in human disease modeling. In this review, we discuss a progress that has been made in modeling inherited arrhythmias and cardiomyopathies, studying molecular mechanisms of the diseases, and searching for and testing drug compounds using patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Engineered heart tissue models from hiPSC-derived cardiomyocytes and cardiac ECM for disease modeling and drug testing applications.Acta Biomater. 2019 Jul 1;92:145-159. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.05.016. Epub 2019 May 7. Acta Biomater. 2019. PMID: 31075518
-
Human Induced Pluripotent Stem-Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes as Models for Genetic Cardiomyopathies.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 6;20(18):4381. doi: 10.3390/ijms20184381. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31489928 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modeling of human cardiomyopathy with induced pluripotent stem cells.J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2014 Oct;10(10):2562-85. doi: 10.1166/jbn.2014.1986. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25992409 Review.
-
Cardiomyopathy in a dish: using human inducible pluripotent stem cells to model inherited cardiomyopathies.J Card Fail. 2015 Sep;21(9):761-70. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2015.04.010. Epub 2015 Apr 28. J Card Fail. 2015. PMID: 25934595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiovascular Disease Modeling Using Patient-Specific Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Aug 12;16(8):18894-922. doi: 10.3390/ijms160818894. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26274955 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Modelling Mitochondrial Disease in Human Pluripotent Stem Cells: What Have We Learned?Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 20;22(14):7730. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147730. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34299348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Taking Systems Medicine to Heart.Circ Res. 2018 Apr 27;122(9):1276-1289. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.310999. Circ Res. 2018. PMID: 29700072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Targeted Metabolomics-Based Assay Using Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes Identifies Structural and Functional Cardiotoxicity Potential.Toxicol Sci. 2020 Apr 1;174(2):218-240. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfaa015. Toxicol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32040181 Free PMC article.
-
New experimental models of the blood-brain barrier for CNS drug discovery.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2017 Jan;12(1):89-103. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2017.1253676. Epub 2016 Nov 7. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2017. PMID: 27782770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptome profiling of 3D co-cultured cardiomyocytes and endothelial cells under oxidative stress using a photocrosslinkable hydrogel system.Acta Biomater. 2017 Aug;58:337-348. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.06.031. Epub 2017 Jun 23. Acta Biomater. 2017. PMID: 28648749 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
