Inter-domain tagging implicates caveolin-1 in insulin receptor trafficking and Erk signaling bias in pancreatic beta-cells
- PMID: 27110488
- PMCID: PMC4837300
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2016.01.009
Inter-domain tagging implicates caveolin-1 in insulin receptor trafficking and Erk signaling bias in pancreatic beta-cells
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Inter-domain tagging implicates caveolin-1 in insulin receptor trafficking and Erk signaling bias in pancreatic beta-cells" [Mol Metab 2016 May; 5 (5): 366-378].Mol Metab. 2024 May;83:101935. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2024.101935. Epub 2024 Apr 8. Mol Metab. 2024. PMID: 38604236 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objective: The role and mechanisms of insulin receptor internalization remain incompletely understood. Previous trafficking studies of insulin receptors involved fluorescent protein tagging at their termini, manipulations that may be expected to result in dysfunctional receptors. Our objective was to determine the trafficking route and molecular mechanisms of functional tagged insulin receptors and endogenous insulin receptors in pancreatic beta-cells.
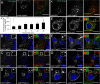
Methods: We generated functional insulin receptors tagged with pH-resistant fluorescent proteins between domains. Confocal, TIRF and STED imaging revealed a trafficking pattern of inter-domain tagged insulin receptors and endogenous insulin receptors detected with antibodies.
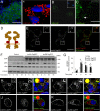
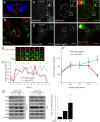
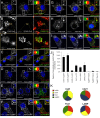
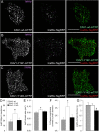
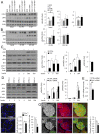
Results: Surprisingly, interdomain-tagged and endogenous insulin receptors in beta-cells bypassed classical Rab5a- or Rab7-mediated endocytic routes. Instead, we found that removal of insulin receptors from the plasma membrane involved tyrosine-phosphorylated caveolin-1, prior to trafficking within flotillin-1-positive structures to lysosomes. Multiple methods of inhibiting caveolin-1 significantly reduced Erk activation in vitro or in vivo, while leaving Akt signaling mostly intact.
Conclusions: We conclude that phosphorylated caveolin-1 plays a role in insulin receptor internalization towards lysosomes through flotillin-1-positive structures and that caveolin-1 helps bias physiological beta-cell insulin signaling towards Erk activation.
Keywords: Autocrine insulin signaling; Insulin receptor internalization; Insulin resistance; Pancreatic islet beta-cells.
Figures
References
-
- Leibiger I.B., Leibiger B., Berggren P.O. Insulin signaling in the pancreatic beta-cell. Annual Review of Nutrition. 2008;28:233–251. - PubMed
-
- Johnson J.D., Alejandro E.U. Control of pancreatic beta-cell fate by insulin signaling: the sweet spot hypothesis. Cell Cycle. 2008;7:1343–1347. - PubMed
-
- Mehran A.E., Templeman N.M., Brigidi G.S., Lim G.E., Chu K.Y., Hu X. Hyperinsulinemia drives diet-induced obesity independently of brain insulin production. Cell Metabolism. 2012;16:723–737. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

