Effect of Etomidate Versus Combination of Propofol-Ketamine and Thiopental-Ketamine on Hemodynamic Response to Laryngoscopy and Intubation: A Randomized Double Blind Clinical Trial
- PMID: 27110526
- PMCID: PMC4834424
- DOI: 10.5812/aapm.30071
Effect of Etomidate Versus Combination of Propofol-Ketamine and Thiopental-Ketamine on Hemodynamic Response to Laryngoscopy and Intubation: A Randomized Double Blind Clinical Trial
Abstract
Background: Laryngoscopy and intubation frequently used for airway management during general anesthesia, is frequently associated with undesirable hemodynamic disturbances.
Objectives: The aim of this study was to compare the effects of etomidate, combination of propofol-ketamine and thiopental-ketamine as induction agents on hemodynamic response to laryngoscopy and intubation.
Patients and methods: In a double blind, randomized clinical trial a total of 120 adult patients of both sexes, aged 18 - 45 years, scheduled for elective surgery under general anesthesia were randomly assigned into three equally sized groups. Patients in group A received etomidate (0.3 mg/kg) plus normal saline as placebo. Patients in group B and C received propofol (1.5 mg/kg) plus ketamine (0.5 mg/kg) and thiopental sodium (3 mg/kg) plus ketamine (0.5 mg/kg), respectively for anesthesia induction. Before laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation, immediately after, and also one and three minutes after the procedures, hemodynamic values (SBP, DBP, MAP and HR) were measured.
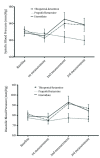
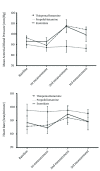
Results: A repeated measurement ANOVA showed significant changes in mean SBP and DBP between the time points (P < 0.05). In addition, the main effect of MAP and HR were statistically significant during the course of study (P < 0.05). Furthermore, after induction of anesthesia, the three study groups had significantly different SBP, DBP and MAP changes overtime (P < 0.05). However, HR changes over time were not statistically significant (P > 0.05). Combination of propofol-ketamine had superior hemodynamic stability compared to other induction agents.
Conclusions: Combination of propofol-ketamine may be recommended as an effective and safe induction agent for attenuating hemodynamic responses to laryngoscopy and intubation with better hemodynamic stability. Although, further well-designed randomized clinical trials to confirm the safety and efficacy of this combination, especially in critically ill patients or patients with cardiovascular disease, are warranted.
Keywords: Etomidate; Hemodynamics; Ketamine; Laryngoscopy; Propofol; Thiopental.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A randomized clinical trial comparing hemodynamic responses to ketamine-propofol combination (ketofol) versus etomidate during anesthesia induction in patients with left ventricular dysfunction undergoing coronary artery bypass graft surgery.Arch Med Sci. 2017 Aug;13(5):1102-1110. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2016.63193. Epub 2016 Oct 25. Arch Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 28883852 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing Hemodynamic Responses to Diazepam, Propofol and Etomidate During Anesthesia Induction in Patients with Left Ventricular Dysfunction Undergoing Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery: a Double-blind, Randomized Clinical Trial.Med Arch. 2017 Jun;71(3):198-203. doi: 10.5455/medarh.2017.71.198-203. Med Arch. 2017. PMID: 28974833 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Hemodynamic responses to etomidate versus ketamine-thiopental sodium combination for anesthetic induction in coronary artery bypass graft surgery patients with low ejection fraction: a double-blind, randomized, clinical trial.J Clin Diagn Res. 2014 Oct;8(10):GC01-5. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2014/10237.5006. Epub 2014 Oct 20. J Clin Diagn Res. 2014. PMID: 25478364 Free PMC article.
-
Induction Agents for Tracheal Intubation in Critically Ill Patients.Crit Care Med. 2025 Jan 1;53(1):e173-e181. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000006506. Epub 2024 Nov 22. Crit Care Med. 2025. PMID: 39774207 Review.
-
Outcomes of Sedative Hypnotic Agents Used for Endotracheal Intubation in Critically Ill Adults: A Systematic Review with Exploratory Meta-Analysis.J Intensive Care Med. 2025 May 14:8850666251337702. doi: 10.1177/08850666251337702. Online ahead of print. J Intensive Care Med. 2025. PMID: 40368347 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of propofol combined with lidocaine on hemodynamics, serum adrenocorticotropic hormone, interleukin-6, and cortisol in children.World J Clin Cases. 2022 Aug 26;10(24):8506-8513. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i24.8506. World J Clin Cases. 2022. PMID: 36157832 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Etomidate Versus Midazolam-Sodium Thiopental on Attenuating the Cardiovascular Response to Laryngoscopy and Tracheal Intubation.Anesth Pain Med. 2024 Mar 14;14(2):e143382. doi: 10.5812/aapm-143382. eCollection 2024 Apr. Anesth Pain Med. 2024. PMID: 39411377 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Ketofol in Blunting Hypotensive Effects of Propofol during Induction and Its Effect on Intraoperative Anesthetic Requirements and Recovery Profile.Anesth Essays Res. 2020 Oct-Dec;14(4):605-610. doi: 10.4103/aer.AER_27_21. Epub 2021 May 27. Anesth Essays Res. 2020. PMID: 34349328 Free PMC article.
-
[Effects of thoracic epidural administration of lidocaine on hemodynamic and arousal responses of double lumen tracheal intubation during induction of anesthesia].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2019 Aug 18;51(4):742-747. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.04.026. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2019. PMID: 31420633 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
A randomized clinical trial comparing hemodynamic responses to ketamine-propofol combination (ketofol) versus etomidate during anesthesia induction in patients with left ventricular dysfunction undergoing coronary artery bypass graft surgery.Arch Med Sci. 2017 Aug;13(5):1102-1110. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2016.63193. Epub 2016 Oct 25. Arch Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 28883852 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Habibi MR, Baradari AG, Soleimani A, Emami Zeydi A, Nia HS, Habibi A, et al. Hemodynamic responses to etomidate versus ketamine-thiopental sodium combination for anesthetic induction in coronary artery bypass graft surgery patients with low ejection fraction: a double-blind, randomized, clinical trial. J Clin Diagn Res. 2014;8(10):GC01–5. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2014/10237.5006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kord Valeshabad A, Nabavian O, Nourijelyani K, Kord H, Vafainejad H, Kord Valeshabad R, et al. Attenuation of Hemodynamic Responses to Laryngoscopy and Tracheal Intubation: Propacetamol versus Lidocaine-A Randomized Clinical Trial. Anesthesiol Res Pract. 2014;2014:170247. doi: 10.1155/2014/170247. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Forbes AM, Dally FG. Acute hypertension during induction of anaesthesia and endotracheal intubation in normotensive man. Br J Anaesth. 1970;42(7):618–24. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases