Dietary Flavonoid Hyperoside Induces Apoptosis of Activated Human LX-2 Hepatic Stellate Cell by Suppressing Canonical NF-κB Signaling
- PMID: 27110557
- PMCID: PMC4826685
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/1068528
Dietary Flavonoid Hyperoside Induces Apoptosis of Activated Human LX-2 Hepatic Stellate Cell by Suppressing Canonical NF-κB Signaling
Abstract
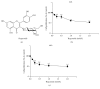
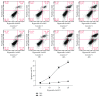
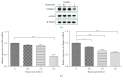
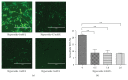
Hyperoside, an active compound found in plants of the genera Hypericum and Crataegus, is reported to exhibit antioxidant, anticancer, and anti-inflammatory activities. Induction of hepatic stellate cell (HSC) apoptosis is recognized as a promising strategy for attenuation of hepatic fibrosis. In this study, we investigated whether hyperoside treatment can exert antifibrotic effects in human LX-2 hepatic stellate cells. We found that hyperoside induced apoptosis in LX-2 cells and decreased levels of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), type I collagen, and intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS). Remarkably, hyperoside also inhibited the DNA-binding activity of the transcription factor NF-κB and altered expression levels of NF-κB-regulated genes related to apoptosis, including proapoptotic genes Bcl-Xs, DR4, Fas, and FasL and anti-apoptotic genes A20, c-IAP1, Bcl-X L , and RIP1. Our results suggest that hyperoside may have potential as a therapeutic agent for the treatment of liver fibrosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Morin, a dietary flavonoid, exhibits anti-fibrotic effect and induces apoptosis of activated hepatic stellate cells by suppressing canonical NF-κB signaling.Biochimie. 2015 Mar;110:107-118. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2015.01.002. Epub 2015 Jan 8. Biochimie. 2015. PMID: 25577997
-
Pien-Tze-Huang ameliorates hepatic fibrosis via suppressing NF-κB pathway and promoting HSC apoptosis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 Nov 15;244:111856. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.111856. Epub 2019 Apr 5. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30959141
-
Wedelolactone exhibits anti-fibrotic effects on human hepatic stellate cell line LX-2.Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Aug 15;714(1-3):105-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.06.012. Epub 2013 Jun 18. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23791612
-
Nuclear erythroid 2-related factor 2: a novel potential therapeutic target for liver fibrosis.Food Chem Toxicol. 2013 Sep;59:421-7. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2013.06.018. Epub 2013 Jun 20. Food Chem Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23793039 Review.
-
Research Progress on Natural Products Alleviating Liver Inflammation and Fibrosis via NF-κB Pathway.Chem Biodivers. 2025 Apr;22(4):e202402248. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202402248. Epub 2025 Jan 3. Chem Biodivers. 2025. PMID: 39576739 Review.
Cited by
-
Chemometric Characterization of Strawberries and Blueberries according to Their Phenolic Profile: Combined Effect of Cultivar and Cultivation System.Molecules. 2019 Nov 26;24(23):4310. doi: 10.3390/molecules24234310. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31779117 Free PMC article.
-
Ursolic acid isolated from Isodon excisoides induces apoptosis and inhibits invasion of GBC-SD gallbladder carcinoma cells.Oncol Lett. 2019 Aug;18(2):1467-1474. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10397. Epub 2019 May 27. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31423212 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical Profiling and Anti-Fibrotic Activities of the Gemmotherapy Bud Extract of Corylus avellana in a Model of Liver Fibrosis on Diabetic Mice.Biomedicines. 2023 Jun 20;11(6):1771. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11061771. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37371866 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperoside ameliorates periodontitis in rats by promoting osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs via activation of the NF-κB pathway.FEBS Open Bio. 2020 Sep;10(9):1843-1855. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12937. Epub 2020 Aug 18. FEBS Open Bio. 2020. PMID: 32687664 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperoside as a Potential Natural Product Targeting Oxidative Stress in Liver Diseases.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jul 25;11(8):1437. doi: 10.3390/antiox11081437. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35892639 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

