Emerging Role and Therapeutic Implication of Wnt Signaling Pathways in Autoimmune Diseases
- PMID: 27110577
- PMCID: PMC4826689
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/9392132
Emerging Role and Therapeutic Implication of Wnt Signaling Pathways in Autoimmune Diseases
Abstract
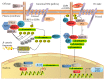
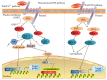
The Wnt signaling pathway plays a key role in many biological aspects, such as cellular proliferation, tissue regeneration, embryonic development, and other systemic effects. Under a physiological condition, it is tightly controlled at different layers and arrays, and a dysregulated activation of this signaling has been implicated into the pathogenesis of various human disorders, including autoimmune diseases. Despite the fact that therapeutic interventions are available for ameliorating disease manifestations, there is no curative therapy currently available for autoimmune disorders. Increasing lines of evidence have suggested a crucial role of Wnt signaling during the pathogenesis of many autoimmune diseases; in addition, some of microRNAs (miRNAs), a class of small, noncoding RNA molecules capable of transcriptionally regulating gene expression, have also recently been demonstrated to possess both physiological and pathological roles in autoimmune diseases by regulating the Wnt signaling pathway. This review summarizes currently our understanding of the pathogenic roles of Wnt signaling in several major autoimmune disorders and miRNAs, those targeting Wnt signaling in autoimmune diseases, with a focus on the implication of the Wnt signaling as potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets in immune diseases, as well as miRNA-mediated regulation of Wnt signaling activation in the development of autoimmune diseases.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

