Interictal epileptiform discharges induce hippocampal-cortical coupling in temporal lobe epilepsy
- PMID: 27111281
- PMCID: PMC4899094
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.4084
Interictal epileptiform discharges induce hippocampal-cortical coupling in temporal lobe epilepsy
Abstract
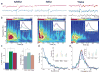
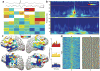
Interactions between the hippocampus and the cortex are critical for memory. Interictal epileptiform discharges (IEDs) identify epileptic brain regions and can impair memory, but the mechanisms by which they interact with physiological patterns of network activity are mostly undefined. We show in a rat model of temporal lobe epilepsy that spontaneous hippocampal IEDs correlate with impaired memory consolidation, and that they are precisely coordinated with spindle oscillations in the prefrontal cortex during nonrapid-eye-movement (NREM) sleep. This coordination surpasses the normal physiological ripple-spindle coupling and is accompanied by decreased ripple occurrence. IEDs also induce spindles during rapid-eye movement (REM) sleep and wakefulness-behavioral states that do not naturally express these oscillations-by generating a cortical 'down' state. In a pilot clinical examination of four subjects with focal epilepsy, we confirm a similar correlation of temporofrontal IEDs with spindles over anatomically restricted cortical regions. These findings imply that IEDs may impair memory via the misappropriation of physiological mechanisms for hippocampal-cortical coupling, which suggests a target for the treatment of memory impairment in epilepsy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




References
-
- Hermann BP, Seidenberg M, Dow C, et al. Cognitive prognosis in chronic temporal lobe epilepsy. Ann Neurol. 2006;60(1):80–87. - PubMed
-
- Ebus S, Arends J, Hendriksen J, et al. Cognitive effects of interictal epileptiform discharges in children. European journal of paediatric neurology : EJPN : official journal of the European Paediatric Neurology Society. 2012;16(6):697–706. - PubMed
-
- Lv Y, Wang Z, Cui L, Ma D, Meng H. Cognitive correlates of interictal epileptiform discharges in adult patients with epilepsy in China. Epilepsy Behav. 2013;29(1):205–210. - PubMed
-
- Binnie CD. Cognitive impairment during epileptiform discharges: is it ever justifiable to treat the EEG? The Lancet. Neurology. 2003;2(12):725–730. - PubMed
-
- Brinciotti M, Matricardi M, Paolella A, Porro G, Benedetti P. Neuropsychological correlates of subclinical paroxysmal EEG activity in children with epilepsy. 1: Qualitative features (generalized and focal abnormalities) Functional neurology. 1989;4(3):235–239. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

