Effects of γ-Aminobutyric Acid Type A Receptor Modulation by Flumazenil on Emergence from General Anesthesia
- PMID: 27111534
- PMCID: PMC5326685
- DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000001134
Effects of γ-Aminobutyric Acid Type A Receptor Modulation by Flumazenil on Emergence from General Anesthesia
Abstract
Background: Transitions into conscious states are partially mediated by inactivation of sleep networks and activation of arousal networks. Pharmacologic hastening of emergence from general anesthesia has largely focused on activating subcortical monoaminergic networks, with little attention on antagonizing the γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor (GABAAR). As the GABAAR mediates the clinical effects of many common general anesthetics, the authors hypothesized that negative GABAAR modulators would hasten emergence, possibly via cortical networks involved in sleep.
Methods: The authors investigated the capacity of the benzodiazepine rescue agent, flumazenil, which had been recently shown to promote wakefulness in hypersomnia patients, to alter emergence. Using an in vivo rodent model and an in vitro GABAAR heterologous expression system, they measured flumazenil's effects on behavioral, neurophysiologic, and electrophysiologic correlates of emergence from isoflurane anesthesia.
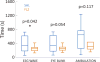
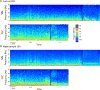
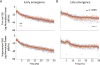
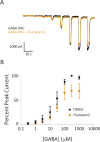
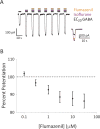
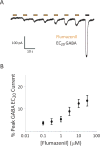
Results: Animals administered intravenous flumazenil (0.4 mg/kg, n = 8) exhibited hastened emergence compared to saline-treated animals (n = 8) at cessation of isoflurane anesthesia. Wake-like electroencephalographic patterns occurred sooner and exhibited more high-frequency electroencephalography power after flumazenil administration (median latency ± median absolute deviation: 290 ± 34 s) compared to saline administration (473 ± 186 s; P = 0.042). Moreover, in flumazenil-treated animals, there was a decreased impact on postanesthesia sleep. In vitro experiments in human embryonic kidney-293T cells demonstrated that flumazenil inhibited isoflurane-mediated GABA current enhancement (n = 34 cells, 88.7 ± 2.42% potentiation at 3 μM). Moreover, flumazenil exhibited weak agonist activity on the GABAAR (n = 10 cells, 10.3 ± 3.96% peak GABA EC20 current at 1 μM).
Conclusions: Flumazenil can modulate emergence from isoflurane anesthesia. The authors highlight the complex role GABAARs play in mediating consciousness and provide mechanistic links between emergence from anesthesia and arousal.
Figures

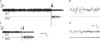

Comment in
-
Flumazenil Modulation of the γ-Aminobutyric Acid Type A Receptor: Competitive versus Noncompetitive Antagonism at the Agonist-binding Site.Anesthesiology. 2017 Feb;126(2):350-351. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000001444. Anesthesiology. 2017. PMID: 28098614 No abstract available.
-
A Rising Tide Lifts All Boats: Increased Ventilation May Be Involved in Accelerated Recovery from Isoflurane Anesthesia after Flumazenil Administration.Anesthesiology. 2017 Feb;126(2):351-352. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000001445. Anesthesiology. 2017. PMID: 28098615 No abstract available.
-
In Reply.Anesthesiology. 2017 Feb;126(2):352-353. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000001446. Anesthesiology. 2017. PMID: 28098616 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

