Gain of Toxicity from ALS/FTD-Linked Repeat Expansions in C9ORF72 Is Alleviated by Antisense Oligonucleotides Targeting GGGGCC-Containing RNAs
- PMID: 27112497
- PMCID: PMC4860075
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.04.006
Gain of Toxicity from ALS/FTD-Linked Repeat Expansions in C9ORF72 Is Alleviated by Antisense Oligonucleotides Targeting GGGGCC-Containing RNAs
Abstract
Hexanucleotide expansions in C9ORF72 are the most frequent genetic cause of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia. Disease mechanisms were evaluated in mice expressing C9ORF72 RNAs with up to 450 GGGGCC repeats or with one or both C9orf72 alleles inactivated. Chronic 50% reduction of C9ORF72 did not provoke disease, while its absence produced splenomegaly, enlarged lymph nodes, and mild social interaction deficits, but not motor dysfunction. Hexanucleotide expansions caused age-, repeat-length-, and expression-level-dependent accumulation of RNA foci and dipeptide-repeat proteins synthesized by AUG-independent translation, accompanied by loss of hippocampal neurons, increased anxiety, and impaired cognitive function. Single-dose injection of antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) that target repeat-containing RNAs but preserve levels of mRNAs encoding C9ORF72 produced sustained reductions in RNA foci and dipeptide-repeat proteins, and ameliorated behavioral deficits. These efforts identify gain of toxicity as a central disease mechanism caused by repeat-expanded C9ORF72 and establish the feasibility of ASO-mediated therapy.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

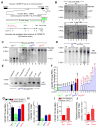


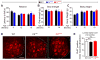

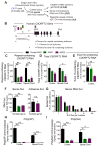

Comment in
-
C9ORF72-ALS/FTD: Transgenic Mice Make a Come-BAC.Neuron. 2016 May 4;90(3):427-31. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.04.026. Neuron. 2016. PMID: 27151634 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI103440/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS089979/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005131/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS087227/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS084528/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008666/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS077402/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS088578/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS063964/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 NS087842/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS088689/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AG000216/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K99 NS091538/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS084974/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

