Human somatic cells subjected to genetic induction with six germ line-related factors display meiotic germ cell-like features
- PMID: 27112843
- PMCID: PMC4844986
- DOI: 10.1038/srep24956
Human somatic cells subjected to genetic induction with six germ line-related factors display meiotic germ cell-like features
Abstract
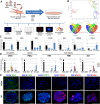
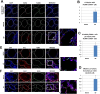
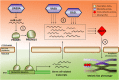
The in vitro derivation of human germ cells has attracted interest in the last years, but their direct conversion from human somatic cells has not yet been reported. Here we tested the ability of human male somatic cells to directly convert into a meiotic germ cell-like phenotype by inducing them with a combination of selected key germ cell developmental factors. We started with a pool of 12 candidates that were reduced to 6, demonstrating that ectopic expression of the germ line-related genes PRDM1, PRDM14, LIN28A, DAZL, VASA and SYCP3 induced direct conversion of somatic cells (hFSK (46, XY), and hMSC (46, XY)) into a germ cell-like phenotype in vitro. Induced germ cell-like cells showed a marked switch in their transcriptomic profile and expressed several post-meiotic germ line related markers, showed meiotic progression, evidence of epigenetic reprogramming, and approximately 1% were able to complete meiosis as demonstrated by their haploid status and the expression of several post-meiotic markers. Furthermore, xenotransplantation assays demonstrated that a subset of induced cells properly colonize the spermatogonial niche. Knowledge obtained from this work can be used to create in vitro models to study gamete-related diseases in humans.
Figures


References
-
- Stephen E. H. & Chandra A. Declining estimates of infertility in the United States: 1982–2002. Fertil Steril 86, 516–523 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Saitou M., Barton S. C. & Surani M. A. A molecular programme for the specification of germ cell fate in mice. Nature 418, 293–300 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Hajkova P. et al.. Epigenetic reprogramming in mouse primordial germ cells. Mech Dev 117, 15–23 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Clark A. T. et al.. Spontaneous differentiation of germ cells from human embryonic stem cells in vitro. Hum Mol Genet 13, 727–739 (2004). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

