Streptococcus oralis Induces Lysosomal Impairment of Macrophages via Bacterial Hydrogen Peroxide
- PMID: 27113357
- PMCID: PMC4936348
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00134-16
Streptococcus oralis Induces Lysosomal Impairment of Macrophages via Bacterial Hydrogen Peroxide
Abstract
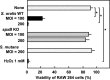
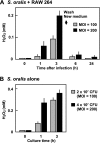
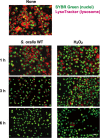
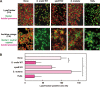
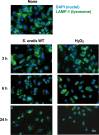
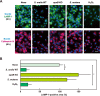
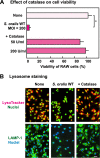
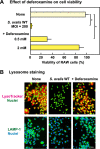
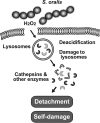
Streptococcus oralis, an oral commensal, belongs to the mitis group of streptococci and occasionally causes opportunistic infections, such as bacterial endocarditis and bacteremia. Recently, we found that the hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) produced by S. oralis is sufficient to kill human monocytes and epithelial cells, implying that streptococcal H2O2 is a cytotoxin. In the present study, we investigated whether streptococcal H2O2 impacts lysosomes, organelles of the intracellular digestive system, in relation to cell death. S. oralis infection induced the death of RAW 264 macrophages in an H2O2-dependent manner, which was exemplified by the fact that exogenous H2O2 also induced cell death. Infection with either a mutant lacking spxB, which encodes pyruvate oxidase responsible for H2O2 production, or Streptococcus mutans, which does not produce H2O2, showed less cytotoxicity. Visualization of lysosomes with LysoTracker revealed lysosome deacidification after infection with S. oralis or exposure to H2O2, which was corroborated by acridine orange staining. Similarly, fluorescent labeling of lysosome-associated membrane protein-1 gradually disappeared during infection with S. oralis or exposure to H2O2 The deacidification and the following induction of cell death were inhibited by chelating iron in lysosomes. Moreover, fluorescent staining of cathepsin B indicated lysosomal destruction. However, treatment of infected cells with a specific inhibitor of cathepsin B had negligible effects on cell death; instead, it suppressed the detachment of dead cells from the culture plates. These results suggest that streptococcal H2O2 induces cell death with lysosomal destruction and then the released lysosomal cathepsins contribute to the detachment of the dead cells.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Microarray analysis of macrophage response to infection with Streptococcus oralis reveals the immunosuppressive effect of hydrogen peroxide.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017 Apr 1;485(2):461-467. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.02.048. Epub 2017 Feb 13. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017. PMID: 28202416
-
Hydrogen peroxide contributes to the epithelial cell death induced by the oral mitis group of streptococci.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 31;9(1):e88136. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088136. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24498253 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen peroxide produced by oral Streptococci induces macrophage cell death.PLoS One. 2013 May 3;8(5):e62563. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062563. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23658745 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the role of Streptococcus oralis as an opportunistic pathogen in infectious diseases.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Nov 4;14:1480961. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1480961. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39559706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Putative pathogenic factors underlying Streptococcus oralis opportunistic infections.J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2025 Apr;58(2):157-163. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2024.09.001. Epub 2024 Sep 6. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2025. PMID: 39261123 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of waterpipe smoking on the salivary microbiome.Front Oral Health. 2023 Nov 9;4:1275717. doi: 10.3389/froh.2023.1275717. eCollection 2023. Front Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 38024144 Free PMC article.
-
Oral streptococci: modulators of health and disease.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Feb 22;14:1357631. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1357631. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38456080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunomodulatory streptococci that inhibit CXCL8 secretion and NFκB activation are common members of the oral microbiota.J Med Microbiol. 2021 Mar;70(3):001329. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.001329. Epub 2021 Mar 18. J Med Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33734952 Free PMC article.
-
Oral streptococci subvert the host innate immune response through hydrogen peroxide.Sci Rep. 2022 Jan 13;12(1):656. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-04562-4. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35027607 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Transformation of C-reactive Protein by Hydrogen Peroxide.J Biol Chem. 2017 Feb 24;292(8):3129-3136. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.773176. Epub 2017 Jan 17. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28096464 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kilian M, Mikkeksen L, Henrichsen J. 1989. Taxonomic study of viridans streptococci: description of Streptococcus gordonii sp. nov. and emended descriptions of Streptococcus sanguis (White and Niven 1946), Streptococcus oralis (Bridge and Sneath 1982), and Streptococcus mitis (Andrewes and Horder 1906). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 39:471–484.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

