Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibition Reduces Albuminuria in Subjects with Overt Diabetic Nephropathy
- PMID: 27113485
- PMCID: PMC5084877
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2015050473
Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibition Reduces Albuminuria in Subjects with Overt Diabetic Nephropathy
Abstract
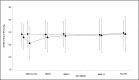
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is the leading cause of ESRD worldwide. Reduced bioavailability or uncoupling of nitric oxide in the kidney, leading to decreased intracellular levels of the nitric oxide pathway effector molecule cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), has been implicated in the progression of DN. Preclinical studies suggest that elevating the cGMP intracellular pool through inhibition of the cGMP-hydrolyzing enzyme phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) might exert renoprotective effects in DN. To test this hypothesis, the novel, highly specific, and long-acting PDE5 inhibitor, PF-00489791, was assessed in a multinational, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel group trial of subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus and overt nephropathy receiving angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker background therapy. In total, 256 subjects with an eGFR between 25 and 60 ml/min per 1.73 m2 and macroalbuminuria defined by a urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio >300 mg/g, were randomly assigned 3:1, respectively, to receive PF-00489791 (20 mg) or placebo orally, once daily for 12 weeks. Using the predefined primary assessment of efficacy (Bayesian analysis with informative prior), we observed a significant reduction in urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio of 15.7% (ratio 0.843; 95% credible interval 0.73 to 0.98) in response to the 12-week treatment with PF-00489791 compared with placebo. PF-00489791 was safe and generally well tolerated in this patient population. Most common adverse events were mild in severity and included headache and upper gastrointestinal events. In conclusion, the safety and efficacy profile of PDE5 inhibitor PF-00489791 supports further investigation as a novel therapy to improve renal outcomes in DN.
Keywords: albuminuria; diabetic nephropathy; nitric oxide; randomized controlled trials.
Copyright © 2016 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Efficacy of a novel inhibitor of vascular adhesion protein-1 in reducing albuminuria in patients with diabetic kidney disease (ALBUM): a randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial.Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018 Dec;6(12):925-933. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(18)30289-4. Epub 2018 Nov 6. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 30413396 Clinical Trial.
-
Rationale, design, and baseline characteristics of ARTS-DN: a randomized study to assess the safety and efficacy of finerenone in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and a clinical diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy.Am J Nephrol. 2014;40(6):572-81. doi: 10.1159/000371497. Epub 2015 Jan 10. Am J Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 25591469 Clinical Trial.
-
The effect of CCR2 inhibitor CCX140-B on residual albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy: a randomised trial.Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015 Sep;3(9):687-96. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(15)00261-2. Epub 2015 Aug 9. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 26268910 Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment of diabetic nephropathy with angiotensin II receptor antagonist.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2003 Mar;7(1):1-8. doi: 10.1007/s101570300000. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2003. PMID: 14586737 Review.
-
Renal protection and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition in microalbuminuric type I and type II diabetic patients.J Hypertens Suppl. 1996 Dec;14(6):S11-4. J Hypertens Suppl. 1996. PMID: 9023709 Review.
Cited by
-
The efficacy of PDE5 inhibitors in diabetic patients.Andrology. 2023 Feb;11(2):245-256. doi: 10.1111/andr.13328. Epub 2022 Dec 9. Andrology. 2023. PMID: 36367281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PDE5 inhibitors and gastric mucosa: implications for the management of peptic ulcer disease.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023 Oct;396(10):2261-2267. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02503-8. Epub 2023 Apr 29. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37119288 Review.
-
Lipids: A Major Culprit in Diabetic Nephropathy.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2024;20(8):60-69. doi: 10.2174/0115733998259273231101052549. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2024. PMID: 38018185 Review.
-
Sildenafil Prevents Podocyte Injury via PPAR-γ-Mediated TRPC6 Inhibition.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017 May;28(5):1491-1505. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2015080885. Epub 2016 Nov 28. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 27895156 Free PMC article.
-
Real-time imaging of cGMP signaling shows pronounced differences between glomerular endothelial cells and podocytes.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 30;14(1):26099. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76768-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39478086 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen L, Magliano DJ, Zimmet PZ: The worldwide epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus--present and future perspectives. Nat Rev Endocrinol 8: 228–236, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Atkins RC, Briganti EM, Lewis JB, Hunsicker LG, Braden G, Champion de Crespigny PJ, DeFerrari G, Drury P, Locatelli F, Wiegmann TB, Lewis EJ: Proteinuria reduction and progression to renal failure in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and overt nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis 45: 281–287, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Eijkelkamp WBA, Zhang Z, Remuzzi G, Parving HH, Cooper ME, Keane WF, Shahinfar S, Gleim GW, Weir MR, Brenner BM, de Zeeuw D: Albuminuria is a target for renoprotective therapy independent from blood pressure in patients with type 2 diabetic nephropathy: post hoc analysis from the Reduction of Endpoints in NIDDM with the Angiotensin II Antagonist Losartan (RENAAL) trial. J Am Soc Nephrol 18: 1540–1546, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Parving HH, Brenner BM, McMurray JJV, de Zeeuw D, Haffner SM, Solomon SD, Chaturvedi N, Persson F, Desai AS, Nicolaides M, Richard A, Xiang Z, Brunel P, Pfeffer MA ALTITUDE Investigators : Cardiorenal end points in a trial of aliskiren for type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 367: 2204–2213, 2012 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

