Squamous precursor lesions of the vulva: current classification and diagnostic challenges
- PMID: 27113549
- PMCID: PMC5518939
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pathol.2016.02.015
Squamous precursor lesions of the vulva: current classification and diagnostic challenges
Abstract
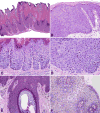
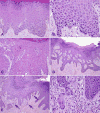
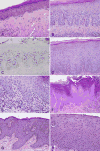
Growing evidence has established two major types of vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN), which correspond to two distinct oncogenic pathways to vulvar squamous cell carcinoma (VSCC). While the incidence of VSCC has remained relatively stable over the last three decades, the incidence of VIN has increased. VIN of usual type (uVIN) is human papillomavirus (HPV)-driven, affects younger women and is a multicentric disease. In contrast, VIN of differentiated type (dVIN) occurs in post-menopausal women and develops independent of HPV infection. dVIN often arises in a background of lichen sclerosus and chronic inflammatory dermatoses. Although isolated dVIN is significantly less common than uVIN, dVIN bears a greater risk for malignant transformation to VSCC and progresses over a shorter time interval. On histological examination, uVIN displays conspicuous architectural and cytological abnormalities, while the morphological features that characterise dVIN are much more subtle and raise a wide differential diagnosis. On the molecular level, dVIN is characterised by a higher number of somatic mutations, particularly in TP53. Here we review the classification, epidemiology, clinical features, histomorphology, ancillary markers and molecular genetics of both types of VIN, and discuss the morphological challenges faced by pathologists in interpreting these lesions.
Keywords: Diagnosis; pathology; precursor; squamous carcinoma in situ; squamous dysplasia; squamous intraepithelial lesion; vulva; vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia.
Copyright © 2016 Royal College of Pathologists of Australasia. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Kosary CL. National Cancer Institute, SEER Program, 1988–2001. Bethesda: National Cancer Institute; 2007. Cancer of the Vulva; pp. 147–154.
-
- Judson PL, Habermann EB, Baxter NN, et al. Trends in the incidence of invasive and in situ vulvar carcinoma. Obstet Gynecol. 2006;107:1018–22. - PubMed
-
- van de Nieuwenhof HP, Massuger LF, van der Avoort IA, et al. Vulvar squamous cell carcinoma development after diagnosis of VIN increases with age. Eur J Cancer. 2009;45:851–6. - PubMed
-
- Scurry J, Wilkinson EJ. Review of terminology of precursors of vulvar squamous cell carcinoma. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2006;10:161–9. - PubMed
-
- Wilkinson EJ, Cox JT, Selim MA, et al. Evolution of terminology for human-papillomavirus-infection-related vulvar squamous intraepithelial lesions. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2015;19:81–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

