Botulinum toxin treatment failures in cervical dystonia: causes, management, and outcomes
- PMID: 27113604
- PMCID: PMC4904718
- DOI: 10.1007/s00415-016-8136-x
Botulinum toxin treatment failures in cervical dystonia: causes, management, and outcomes
Abstract
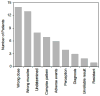
Botulinum toxin (BoNT) is highly effective in the treatment of cervical dystonia (CD), yet a significant proportion of patients report low levels of satisfaction following treatment and fail to follow up for repeated treatments. The goal of this study was to determine the reasons that some patients have unsatisfactory responses. A total of 35 subjects who came to our center requesting alternative treatments due to unsatisfactory responses following BoNT treatment for CD were evaluated. Included were 26 women and 9 men with an average age of 57.1 years (range 25-82 years), and an average duration of illness of 12.5 years (range 1-55 years). Details of unsatisfactory BoNT treatments were methodically collected by a movement specialist using a standardized intake form, including provider subspecialty, product used, the number of satisfactory or unsatisfactory trials, doses given, specific muscles treated, the use of electromyographic guidance, side effects, and tests of resistance. The specialist then provided repeat treatments if indicated, and followed each case until the reasons for unsatisfactory outcomes could be determined. Multiple reasons for unsatisfactory outcomes were found. They included suboptimal BoNT doses, suboptimal muscle targeting, intolerable side effects, complex movement patterns, discordant perceptions, and incorrect diagnoses. Only one patient was functionally resistant to BoNT. Of 32 subjects who received repeat BoNT treatments, 25 (78 %) achieved satisfactory responses after revision of the original treatment plan. These results indicate that the majority of unsatisfactory responses to BoNT treatment of CD were caused by correctible factors and imply a need for improved education regarding optimal treatment methods.
Keywords: Botulinum toxin; Treatment failure; Treatment resistance.
Figures
References
-
- Evatt ML, Freeman A, Factor S. Adult-onset dystonia. Handb Clin Neurol. 2011;100:481–511. - PubMed
-
- Hallett M, Albanese A, Dressler D, et al. Evidence-based review and assessment of botulinum neurotoxin for the treatment of movement disorders. Toxicon. 2013;67:94–114. - PubMed
-
- Sethi KD, Rodriguez R, Olayinka B. Satisfaction with botulinum toxin treatment: a cross-sectional survey of patients with cervical dystonia. J Med Econ. 2012;15:419–23. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

