A thrombopoietin receptor antagonist is capable of depleting myelofibrosis hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells
- PMID: 27114459
- PMCID: PMC4929928
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2015-10-674465
A thrombopoietin receptor antagonist is capable of depleting myelofibrosis hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells
Erratum in
-
Wang X, Haylock D, Hu CS, et al. A thrombopoietin receptor antagonist is capable of depleting myelofibrosis hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. Blood. 2016;127(26):3398-3409.Blood. 2017 Dec 21;130(25):2809. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-11-815340. Blood. 2017. PMID: 29269535 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
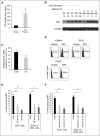
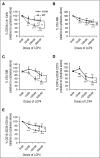
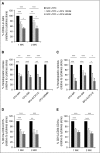
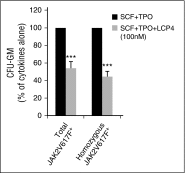
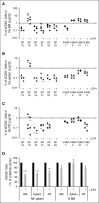
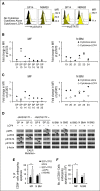
Recently, interactions between thrombopoietin (TPO) and its receptor, the myeloproliferative leukemia (MPL) virus oncogene, have been shown to play a role in the development and progression of myeloproliferative neoplasms including myelofibrosis (MF). These observations have led to the development of strategies to disrupt the association of TPO with its receptor as a means of targeting MF hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and hematopoietic progenitor cells (HPCs). In this report, we show that although both splenic and peripheral blood MF CD34(+) cells expressed lower levels of MPL than normal CD34(+) cells, TPO promoted the proliferation of MF CD34(+) cells and HPCs in a dose-dependent fashion. Furthermore, the treatment of MF but not normal CD34(+) cells with a synthesized MPL antagonist, LCP4, decreased the number of CD34(+)Lin(-) cells and all classes of assayable HPCs (colony-forming unit-megakaryocyte [CFU-MK], CFU-granulocyte/macrophage, burst-forming unit-erythroid/CFU-erythroid, and CFU-granulocyte/erythroid/macrophage/MK) irrespective of their mutational status. In addition, LCP4 treatment resulted in the depletion of the number of MF HPCs that were JAK2V617F(+) Moreover, the degree of human cell chimerism and the proportion of malignant donor cells were significantly reduced in immunodeficient mice transplanted with MF CD34(+) cell grafts treated with LCP4. These effects of LCP4 on MF HSCs/HPCs were associated with inhibition of JAK-STAT activity, leading to the induction of apoptosis. These findings demonstrate that such specific anti-cytokine receptor antagonists represent a new class of drugs that are capable of targeting MF HSCs.
© 2016 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures
References
-
- Klampfl T, Gisslinger H, Harutyunyan AS, et al. Somatic mutations of calreticulin in myeloproliferative neoplasms. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(25):2379–2390. - PubMed
-
- Tefferi A, Lasho TL, Finke CM, et al. CALR vs JAK2 vs MPL-mutated or triple-negative myelofibrosis: clinical, cytogenetic and molecular comparisons. Leukemia. 2014;28(7):1472–1477. - PubMed
-
- Tefferi A. Myelofibrosis with myeloid metaplasia. N Engl J Med. 2000;342(17):1255–1265. - PubMed
-
- Yoshihara H, Arai F, Hosokawa K, et al. Thrombopoietin/MPL signaling regulates hematopoietic stem cell quiescence and interaction with the osteoblastic niche. Cell Stem Cell. 2007;1(6):685–697. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

