Transcription factor KLF2 regulates homeostatic NK cell proliferation and survival
- PMID: 27114551
- PMCID: PMC4868471
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1521491113
Transcription factor KLF2 regulates homeostatic NK cell proliferation and survival
Abstract
Natural killer (NK) cells are innate lymphocytes that recognize and lyse virally infected or transformed cells. This latter property is being pursued in clinics to treat leukemia with the hope that further breakthroughs in NK cell biology can extend treatments to other cancers. At issue is the ability to expand transferred NK cells and prolong their functionality within the context of a tumor. In terms of NK cell expansion and survival, we now report that Kruppel-like factor 2 (KLF2) is a key transcription factor that underpins both of these events. Excision of Klf2 using gene-targeted mouse models promotes spontaneous proliferation of immature NK cells in peripheral tissues, a phenotype that is replicated under ex vivo conditions. Moreover, KLF2 imprints a homeostatic migration pattern on mature NK cells that allows these cells to access IL-15-rich microenvironments. KLF2 accomplishes this feat within the mature NK cell lineage via regulation of a subset of homing receptors that respond to homeostatic ligands while leaving constitutively expressed receptors that recognize inflammatory cytokines unperturbed. Under steady-state conditions, KLF2-deficient NK cells alter their expression of homeostatic homing receptors and subsequently undergo apoptosis due to IL-15 starvation. This novel mechanism has implications regarding NK cell contraction following the termination of immune responses including the possibility that retention of an IL-15 transpresenting support system is key to extending NK cell activity in a tumor environment.
Keywords: IL-15; KLF2; NK cell; NK cell homeostasis; NK cell proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


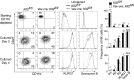
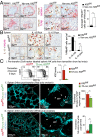
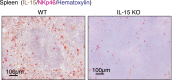
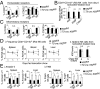
Similar articles
-
KLF12 Regulates Mouse NK Cell Proliferation.J Immunol. 2019 Aug 15;203(4):981-989. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1900396. Epub 2019 Jul 12. J Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31300511 Free PMC article.
-
NK cells delay allograft rejection in lymphopenic hosts by downregulating the homeostatic proliferation of CD8+ T cells.J Immunol. 2010 Jun 15;184(12):6649-57. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0903729. Epub 2010 May 14. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20483732
-
Nfil3-independent lineage maintenance and antiviral response of natural killer cells.J Exp Med. 2013 Dec 16;210(13):2981-90. doi: 10.1084/jem.20130417. Epub 2013 Nov 25. J Exp Med. 2013. PMID: 24277151 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering Natural Killer Cell Homeostasis.Front Immunol. 2020 May 12;11:812. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00812. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32477340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The unconventional expression of IL-15 and its role in NK cell homeostasis.Immunol Cell Biol. 2014 Mar;92(3):210-3. doi: 10.1038/icb.2014.1. Epub 2014 Feb 4. Immunol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24492800 Review.
Cited by
-
Reprogramming the tumor microenvironment by genome editing for precision cancer therapy.Mol Cancer. 2022 Apr 11;21(1):98. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01561-5. Mol Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35410257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deconstructing deployment of the innate immune lymphocyte army for barrier homeostasis and protection.Immunol Rev. 2018 Nov;286(1):6-22. doi: 10.1111/imr.12709. Immunol Rev. 2018. PMID: 30294966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spontaneously Resolved Atopic Dermatitis Shows Melanocyte and Immune Cell Activation Distinct From Healthy Control Skin.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 24;12:630892. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.630892. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33717163 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of hub lncRNAs in head and neck cancer based on weighted gene co-expression network analysis and experiments.FEBS Open Bio. 2021 Jul;11(7):2060-2073. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13134. Epub 2021 May 21. FEBS Open Bio. 2021. PMID: 33660438 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factor KLF2 is associated with the dysfunctional status of NK cells and the prognosis of pediatric B-ALL patients.Front Oncol. 2025 Jan 21;14:1456004. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1456004. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39906661 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Miller JS, et al. Successful adoptive transfer and in vivo expansion of human haploidentical NK cells in patients with cancer. Blood. 2005;105(8):3051–3057. - PubMed
-
- Walzer T, Vivier E. G-protein-coupled receptors in control of natural killer cell migration. Trends Immunol. 2011;32(10):486–492. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

