Patient considerations and drug selection in the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 27114711
- PMCID: PMC4833375
- DOI: 10.2147/TCRM.S81144
Patient considerations and drug selection in the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
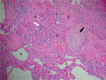
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a progressive interstitial lung disease of unknown cause. Approximately 5,000 people are diagnosed with IPF in the UK every year. People with IPF suffer significant morbidity and, without any curative treatment at present, survival rates remain poor with a median survival of 3 years. While treatment remains largely supportive, many drug therapies have been trialed in IPF over the years. Pirfenidone and nintedanib are newly licensed treatments for IPF and the first drugs to have shown convincing evidence of slowing disease progression. In addition to evaluating clinical evidence, we also discuss elements affecting drug choice from the viewpoint of patients and health care professionals. We discuss pharmacological and nonpharmacological aspects of providing best supportive care for patients with IPF. However, few good quality studies exist focusing on controlling symptoms specifically in patients with IPF, and recommendations are often extrapolated from evidence in other chronic diseases. In covering these topics, we hope to provide readers with a comprehensive review of the available evidence pertaining to all aspects of care for patients suffering with IPF.
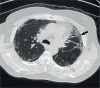
Keywords: clinical trials; decision making; forced vital capacity; high-resolution computed tomography; idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; interstitial lung disease; usual interstitial pneumonia.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Comparison of the Effectiveness of Nintedanib and Pirfenidone in Treating Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2024 Feb 15;16(2):e54268. doi: 10.7759/cureus.54268. eCollection 2024 Feb. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38500898 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological management of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: current and emerging options.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2021 Feb;22(2):191-204. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2020.1822326. Epub 2020 Sep 29. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 32993388 Review.
-
Survival of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and pulmonary hypertension under therapy with nintedanib or pirfenidone.Intern Emerg Med. 2022 Apr;17(3):815-822. doi: 10.1007/s11739-021-02883-w. Epub 2021 Nov 16. Intern Emerg Med. 2022. PMID: 34787802
-
Real-life experiences in a single center: efficacy of pirfenidone in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and fibrotic idiopathic non-specific interstitial pneumonia patients.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2020 Jan-Dec;14:1753466620963015. doi: 10.1177/1753466620963015. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2020. PMID: 33070705 Free PMC article.
-
Using Data on Survival with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis to Estimate Survival with Other Types of Progressive Fibrosis Interstitial Lung Disease: A Bayesian Framework.Adv Ther. 2022 Feb;39(2):1045-1054. doi: 10.1007/s12325-021-02014-z. Epub 2021 Dec 27. Adv Ther. 2022. PMID: 34957531 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Physician characteristics associated with treatment initiation patterns in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Chron Respir Dis. 2019 Jan-Dec;16:1479973119879678. doi: 10.1177/1479973119879678. Chron Respir Dis. 2019. PMID: 31558049 Free PMC article.
-
Validity of the Patient Experiences and Satisfaction with Medications (PESaM) Questionnaire.Patient. 2019 Feb;12(1):149-162. doi: 10.1007/s40271-018-0340-6. Patient. 2019. PMID: 30367435 Free PMC article.
-
The effects and safety of pirfenidone in the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a meta-analysis and systematic review.Eur J Med Res. 2021 Oct 30;26(1):129. doi: 10.1186/s40001-021-00601-y. Eur J Med Res. 2021. PMID: 34717762 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Pretesting of a Questionnaire to Assess Patient Experiences and Satisfaction with Medications (PESaM Questionnaire).Patient. 2017 Oct;10(5):629-642. doi: 10.1007/s40271-017-0234-z. Patient. 2017. PMID: 28357591 Free PMC article.
-
A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Nintedanib in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis in the UK.Pharmacoeconomics. 2017 Apr;35(4):479-491. doi: 10.1007/s40273-016-0480-2. Pharmacoeconomics. 2017. PMID: 28039616 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Navaratnam V, Fleming KM, West J, et al. The rising incidence of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in the U.K. Thorax. 2011;66(6):462–467. - PubMed
-
- Selman M, King TE, Pardo A. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: prevailing and evolving hypotheses about its pathogenesis and implications for therapy. Ann Intern Med. 2001;134(2):136–151. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

