In-hospital and six-month outcomes of elderly patients undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention for acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction
- PMID: 27114734
- PMCID: PMC4834178
In-hospital and six-month outcomes of elderly patients undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention for acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction
Abstract
Background: Elderly patients constitute a rapidly growing proportion of the population, and hence the increasing rises in the number of patients with ST-segment-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). Primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), which is now established as the preferred reperfusion strategy in STEMI patients, has been inadequately investigated in this high-risk group. The aim of the present study was to investigate the in-hospital and 6-month outcomes of primary PCI in elderly patients (≥ 75 years) with STEMI.
Methods: A total of 100 elderly patients with STEMI including those with cardiogenic shock were included. Primary PCI procedures were performed in a tertiary referral center between 2009 and 2014. In-hospital and 6-month outcomes of patients were recorded and analyzed.
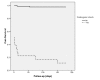
Results: The average age of the patients was 79.6 ± 3.8 years (range = 75-90 years) and 27.0% were women. Cardiovascular risk factors and prior events were common. Nearly, half of the patients had three-vessel disease and the left anterior descending artery (LAD) was the most common infarct-related artery. The presence of cardiogenic shock but not the other variables was associated with less anatomic and procedural success (P < 0.001). It was also the major independent predictors of 6-month mortality in the patients aged ≥ 75 years, [hazard ratio (HR) = 8.02; 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.75-25.97, P < 0.001]. In-hospital mortality was 2.4% in the patients without and 83.0% in those with cardiogenic shock.
Conclusion: Primary PCI in aged patients could be associated with low complication rates and improved survival if performed in high-volume centers with experienced operators. Considering the very high rate of mortality in patients with cardiogenic shock, there should be measures to treat these patients before the onset of hemodynamic instability.
Keywords: Cardiogenic Shock; Elderly; Percutaneous Coronary Intervention.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multivessel Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Patients With ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction With Cardiogenic Shock.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018 Feb 27;71(8):844-856. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2017.12.028. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 29471935
-
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Older Patients With ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction and Cardiogenic Shock.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019 Apr 23;73(15):1890-1900. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.01.055. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 30999991 Free PMC article.
-
Primary percutaneous coronary intervention for acute ST elevation myocardial infarction: Outcomes and determinants of outcomes: A tertiary care center study from North India.Indian Heart J. 2017 May-Jun;69(3):294-298. doi: 10.1016/j.ihj.2016.11.322. Epub 2016 Nov 30. Indian Heart J. 2017. PMID: 28648416 Free PMC article.
-
Culprit Vessel-Only Versus Multivessel Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Patients With Cardiogenic Shock Complicating ST-Segment-Elevation Myocardial Infarction: A Collaborative Meta-Analysis.Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2017 Nov;10(11):e005582. doi: 10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.117.005582. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2017. PMID: 29146672 Review.
-
Radial versus femoral access for primary percutaneous interventions in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction patients: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2013 Aug;6(8):814-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2013.04.010. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2013. PMID: 23968700 Review.
Cited by
-
Myocardial Infarction in Iran: Epidemiology, Management, and Prognosis.J Tehran Heart Cent. 2023 Apr;18(2):82-86. doi: 10.18502/jthc.v18i2.13316. J Tehran Heart Cent. 2023. PMID: 37637282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Determination of risk factors affecting the in-hospital prognosis of patients with acute ST segment elevation myocardial infarction after percutaneous coronary intervention.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2017 Sep 12;17(1):243. doi: 10.1186/s12872-017-0660-9. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2017. PMID: 28899364 Free PMC article.
-
In-Hospital Clinical Outcomes and Procedural Complications of Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Elderly Patients.Cardiol Res. 2017 Oct;8(5):199-205. doi: 10.14740/cr582e. Epub 2017 Oct 27. Cardiol Res. 2017. PMID: 29118881 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Different Methods of Administration of Diltiazem on Clinical Efficacy in Patients with Acute ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction.Med Sci Monit. 2018 Sep 17;24:6544-6550. doi: 10.12659/MSM.912576. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 30223281 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Public health and aging: trends in aging - united states and worldwide. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2003;52(6):101–6. - PubMed
-
- van de Werf F, Ardissino D, Betriu A, Cokkinos DV, Falk E, Fox KA, et al. Management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation. European Heart Journal. 2003;24(1):28–66. - PubMed
-
- Alexander KP, Newby LK, Armstrong PW, Cannon CP, Gibler WB, Rich MW, et al. Acute coronary care in the elderly, part II: ST-segment-elevation myocardial infarction: a scientific statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association Council on Clinical Cardiology: in collaboration with the Society of Geriatric Cardiology. Circulation. 2007;115(19):2570–89. - PubMed
-
- O'Gara PT, Kushner FG, Ascheim DD, Casey DE, Chung MK, de Lemos JA, et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of ST-elevation myocardial infarction: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2013;127(4):529–55. - PubMed
-
- Gurwitz JH, Col NF, Avorn J. The exclusion of the elderly and women from clinical trials in acute myocardial infarction. JAMA. 1992;268(11):1417–22. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous