Combined sequence and sequence-structure based methods for analyzing FGF23, CYP24A1 and VDR genes
- PMID: 27114920
- PMCID: PMC4833053
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mgene.2016.03.005
Combined sequence and sequence-structure based methods for analyzing FGF23, CYP24A1 and VDR genes
Abstract
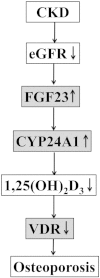
FGF23, CYP24A1 and VDR altogether play a significant role in genetic susceptibility to chronic kidney disease (CKD). Identification of possible causative mutations may serve as therapeutic targets and diagnostic markers for CKD. Thus, we adopted both sequence and sequence-structure based SNP analysis algorithm in order to overcome the limitations of both methods. We explore the functional significance towards the prediction of risky SNPs associated with CKD. We assessed the performance of four widely used pathogenicity prediction methods. We compared the performances of the programs using Mathews correlation Coefficient ranged from poor (MCC = 0.39) to reasonably good (MCC = 0.42). However, we got the best results for the combined sequence and structure based analysis method (MCC = 0.45). 4 SNPs from FGF23 gene, 8 SNPs from VDR gene and 13 SNPs from CYP24A1 gene were predicted to be the causative agents for human diseases. This study will be helpful in selecting potential SNPs for experimental study from the SNP pool and also will reduce the cost for identification of potential SNPs as a genetic marker.
Keywords: CYP24A1; Chronic kidney disease; Combined sequence and sequence-structure based methods; FGF23; SNP analysis; VDR.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Combined sequence and sequence-structure-based methods for analyzing RAAS gene SNPs: a computational approach.J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2014 Dec;34(6):513-26. doi: 10.3109/10799893.2014.922575. Epub 2014 May 30. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2014. PMID: 24878201
-
E-pharmacophore filtering and molecular dynamics simulation studies in the discovery of potent drug-like molecules for chronic kidney disease.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2016 Oct;34(10):2233-2250. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2015.1111168. Epub 2016 Mar 11. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2016. PMID: 26513595
-
Vitamin D-Related Gene Polymorphisms, Plasma 25-Hydroxy-Vitamin D, Cigarette Smoke and Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Risk.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Sep 22;17(10):1597. doi: 10.3390/ijms17101597. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27669215 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D and type II sodium-dependent phosphate cotransporters.Contrib Nephrol. 2013;180:86-97. doi: 10.1159/000346786. Epub 2013 May 6. Contrib Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 23652552 Review.
-
Parathyroid function in chronic kidney disease: role of FGF23-Klotho axis.Contrib Nephrol. 2013;180:110-23. doi: 10.1159/000346791. Epub 2013 May 3. Contrib Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 23652554 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional and Structural Impact of Deleterious Missense Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in the NR3C1, CYP3A5, and TNF-α Genes: An In Silico Analysis.Biomolecules. 2022 Sep 16;12(9):1307. doi: 10.3390/biom12091307. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36139147 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ADHR Consortium Autosomal dominant hypophosphataemic rickets is associated with mutations in FGF23. Nat. Genet. 2000;26:345–348. - PubMed
-
- Ahmad S., Gromiha M.M., Sarai A. Real value prediction of solvent accessibility from amino acid sequence. Proteins. 2003;50:629–635. - PubMed
-
- Bai X.Y., Miao D., Goltzman D., Karaplis A.C. The autosomal dominant hypophosphatemic rickets R176Q mutation in fibroblast growth factor 23 resists proteolytic cleavage and enhances in vivo biological potency. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:9843–9849. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

