Towards the Application of Fuzzy Logic for Developing a Novel Indoor Air Quality Index (FIAQI)
- PMID: 27114985
- PMCID: PMC4841875
Towards the Application of Fuzzy Logic for Developing a Novel Indoor Air Quality Index (FIAQI)
Abstract
Background: In the past few decades, Indoor Air Pollution (IAP) has become a primary concern to the point. It is increasingly believed to be of equal or greater importance to human health compared to ambient air. However, due to the lack of comprehensive indices for the integrated assessment of indoor air quality (IAQ), we aimed to develop a novel, Fuzzy-Based Indoor Air Quality Index (FIAQI) to bridge the existing gap in this area.
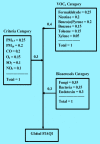
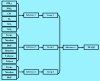
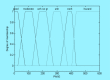
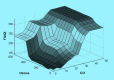
Methods: We based our index on fuzzy logic, which enables us to overcome the limitations of traditional methods applied to develop environmental quality indices. Fifteen parameters, including the criteria air pollutants, volatile organic compounds, and bioaerosols were included in the FIAQI due mainly to their significant health effects. Weighting factors were assigned to the parameters based on the medical evidence available in the literature on their health effects. The final FIAQI consisted of 108 rules. In order to demonstrate the performance of the index, data were intentionally generated to cover a variety of quality levels. In addition, a sensitivity analysis was conducted to assess the validity of the index.
Results: The FIAQI tends to be a comprehensive tool to classify IAQ and produce accurate results.
Conclusion: It seems useful and reliable to be considered by authorities to assess IAQ environments.
Keywords: Fuzzy-based indoor air quality index (FIAQI); Indoor air pollution (IAP); Indoor air quality (IAQ).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Indoor air quality in a metropolitan area metro using fuzzy logic assessment system.Sci Total Environ. 2013 Apr 1;449:461-9. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.12.043. Epub 2013 Mar 6. Sci Total Environ. 2013. PMID: 23467101
-
Evaluation of Indoor Air Quality Screening Strategies: A Step-Wise Approach for IAQ Screening.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2016 Dec 14;13(12):1240. doi: 10.3390/ijerph13121240. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2016. PMID: 27983667 Free PMC article.
-
Classifying Sources Influencing Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) Using Artificial Neural Network (ANN).Sensors (Basel). 2015 May 20;15(5):11665-84. doi: 10.3390/s150511665. Sensors (Basel). 2015. PMID: 26007724 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Indoor Air Quality Problems in Office-Like Environments: Role of Occupational Health Services.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018 Apr 12;15(4):741. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15040741. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018. PMID: 29649167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation and its role in the prevention of building-associated illness.Occup Med. 1989 Oct-Dec;4(4):741-52. Occup Med. 1989. PMID: 2690385 Review.
Cited by
-
Study of the Characteristics and Comprehensive Fuzzy Assessment of Indoor Air Chemical Contamination in Public Buildings.Front Public Health. 2021 May 5;9:579299. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.579299. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34026697 Free PMC article.
-
ADFIST: Adaptive Dynamic Fuzzy Inference System Tree Driven by Optimized Knowledge Base for Indoor Air Quality Assessment.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jan 28;22(3):1008. doi: 10.3390/s22031008. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35161754 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of classroom microclimate in context to health-related national and international indoor air quality standards.Front Public Health. 2024 Aug 12;12:1440376. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1440376. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39188796 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smith KR. (2002). Indoor air pollution in developing countries: recommendations for research†. Indoor Air, 2 ( 3): 198–207. - PubMed
-
- Heinrich J. (2011). Influence of indoor factors in dwellings on the development of childhood asthma. Int J Hyg Environ Health, 214: 1–25. - PubMed
-
- Brasche S, Bischof W. (2005). Daily time spent indoors in German homes—baseline data for the assessment of indoor exposure of German occupants. Int J Hyg Environ Health, 208: 247–253. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein JA, Alexis N, Bacchus H, Bernstein IL, Fritz P, Horner E, Tarlo MS. (2008). The health effects of nonindustrial indoor air pollution. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 121: 585–591. - PubMed
-
- Colls J, Tiwary A. (2010). Air Pollution measurement, modelling and mitigation , 3rd ed. London & New York: : Routledge; .
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
