Living donor liver transplantation in Egypt
- PMID: 27115003
- PMCID: PMC4824739
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2304-3881.2015.10.03
Living donor liver transplantation in Egypt
Abstract
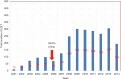
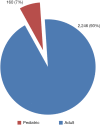
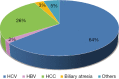
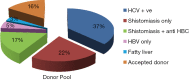
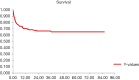
In Egypt there is no doubt that chronic liver diseases are a major health concern. Hepatitis C virus (HCV) prevalence among the 15-59 years age group is estimated to be 14.7%. The high prevalence of chronic liver diseases has led to increasing numbers of Egyptian patients suffering from end stage liver disease (ESLD), necessitating liver transplantation (LT). We reviewed the evolution of LT in Egypt and the current status. A single center was chosen as an example to review the survival and mortality rates. To date, deceased donor liver transplantation (DDLT) has not been implemented in any program though Egyptian Parliament approved the law in 2010. Living donor liver transplantation (LDLT) seemed to be the only logical choice to save many patients who are in desperate need for LT. By that time, there was increase in number of centers doing LDLT (13 centers) and increase in number of LDLT cases [2,400] with improvement of the results. Donor mortality rate is 1.66 per 1,000 donors; this comprised four donors in the Egyptian series. The exact recipient survival is not accurately known however, and the one-year, three-year and five-year survival were 73.17%, 70.83% and 64.16% respectively in the International Medical Center (IMC) in a series of 145 adult to adult living donor liver transplantation (AALDLT) cases. There was no donor mortality in this series. LDLT are now routinely and successfully performed in Egypt with reasonable donor and recipient outcomes. Organ shortage remains the biggest hurdle facing the increasing need for LT. Although LDLT had reasonable outcomes, it carries considerable risks to healthy donors. For example, it lacks cadaveric back up, and is not feasible for all patients. The initial success in LDLT should drive efforts to increase the people awareness about deceased organ donation in Egypt.
Keywords: Egypt; Liver; living donor liver transplantation (LDLT); transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evolution of living donor liver transplantation in Egypt.Saudi Med J. 2005 Sep;26(9):1394-7. Saudi Med J. 2005. PMID: 16155655
-
Does living donation have advantages over deceased donation in liver transplantation?J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010 Oct;25(10):1598-603. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2010.06418.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010. PMID: 20880167 Review.
-
Living-Donor Liver Transplantation in Hepatitis C Virus Era: A Report of 500 Consecutive Cases in a Single Center.Transplant Proc. 2018 Jun;50(5):1396-1406. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2018.02.085. Epub 2018 Mar 10. Transplant Proc. 2018. PMID: 29880362
-
Living donor liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma.Recent Results Cancer Res. 2013;190:165-79. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-16037-0_11. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 22941020
-
Liver Transplantation: East versus West.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2013 Sep;3(3):243-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2013.08.004. Epub 2013 Sep 12. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 25755506 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Occult HCV infection in liver transplanted patients: frequency and consequences.Clin Exp Hepatol. 2022 Jun;8(2):125-131. doi: 10.5114/ceh.2022.115116. Epub 2022 Apr 5. Clin Exp Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 36092754 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and predictors of post-liver transplantation metabolic bone diseases.Clin Exp Hepatol. 2021 Sep;7(3):286-292. doi: 10.5114/ceh.2021.109412. Epub 2021 Oct 11. Clin Exp Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 34712830 Free PMC article.
-
BAR Score Performance in Predicting Survival after Living Donor Liver Transplantation: A Single-Center Retrospective Study.Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Feb 18;2022:2877859. doi: 10.1155/2022/2877859. eCollection 2022. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35223683 Free PMC article.
-
Live donor liver transplantation for alcoholic hepatitis.Hepatol Int. 2017 Jan;11(1):34-37. doi: 10.1007/s12072-016-9770-1. Epub 2016 Oct 6. Hepatol Int. 2017. PMID: 27714680
-
Egyptian protocol for living donor liver transplantation (LDLT) during SARS-CoV-2 pandemic.Egypt Liver J. 2021;11(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s43066-020-00074-4. Epub 2021 Feb 9. Egypt Liver J. 2021. PMID: 34777866 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Strong RW, Lynch SV, Ong TH, et al. Successful Liver Transplantation from a Living Donor to Her Son. N Engl J Med 1990;322:1505-7. - PubMed
-
- Hashikura Y, Makuuchi M, Kawasaki S, et al. Successful living-related partial liver transplantation to an adult patient. Lancet 1994;343:1233-4. - PubMed
-
- Lee SG. Living-donor liver transplantation in adults. Br Med Bull 2010;94:33-48. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
