Coupling of dyspnea perception and occurrence of tachypnea during exercise
- PMID: 27117877
- PMCID: PMC10717682
- DOI: 10.1007/s12576-016-0452-5
Coupling of dyspnea perception and occurrence of tachypnea during exercise
Abstract
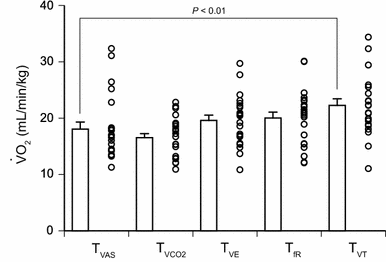
During exercise, tidal volume initially contributes to ventilatory responses more than respiratory frequency, and respiratory frequency then increases rapidly while tidal volume stabilizes. Dyspnea intensity is also known to increase in a threshold-like manner. We tested the possibility that the threshold of tachypneic breathing is equal to that of dyspnea perception during cycle ergometer exercise (n = 27). Dyspnea intensity was scored by a visual analog scale. Thresholds were expressed as values of pulmonary O2 uptake at each breakpoint. Dyspnea intensity and respiratory frequency started increasing rapidly once the intensity of stimuli exceeded a threshold level. The thresholds for dyspnea intensity and for occurrence of tachypnea were significantly correlated. An intraclass correlation coefficient of 0.71 and narrow limits of agreement on the Bland-Altman plot indicated a good agreement between these thresholds. These results suggest that the start of tachypneic breathing coincides with the threshold for dyspnea intensity during cycle ergometer exercise.
Keywords: Dyspnea; Exercise hyperpnea; Pulmonary O2 uptake; Respiratory frequency; Tachypnea.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Dejours P. Neurogenic factors in the control of ventilation during exercise. Circ Res. 1967;20(Suppl 1):146–153.
-
- Haouzi P (2006) Counterpoint: supraspinal locomotor centers do not contribute significantly to the hyperpnea of dynamic exercise. J Appl Physiol 100: 1079–1082; (discussion 1082–1073) - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

