Memory retrieval of inhibitory avoidance requires histamine H1 receptor activation in the hippocampus
- PMID: 27118833
- PMCID: PMC4868453
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1604841113
Memory retrieval of inhibitory avoidance requires histamine H1 receptor activation in the hippocampus
Abstract
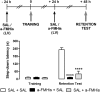
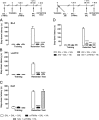
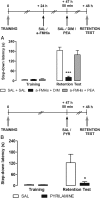
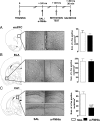
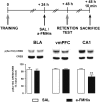
Retrieval represents a dynamic process that may require neuromodulatory signaling. Here, we report that the integrity of the brain histaminergic system is necessary for retrieval of inhibitory avoidance (IA) memory, because rats depleted of histamine through lateral ventricle injections of α-fluoromethylhistidine (a-FMHis), a suicide inhibitor of histidine decarboxylase, displayed impaired IA memory when tested 2 d after training. a-FMHis was administered 24 h after training, when IA memory trace was already formed. Infusion of histamine in hippocampal CA1 of brain histamine-depleted rats (hence, amnesic) 10 min before the retention test restored IA memory but was ineffective when given in the basolateral amygdala (BLA) or the ventral medial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC). Intra-CA1 injections of selective H1 and H2 receptor agonists showed that histamine exerted its effect by activating the H1 receptor. Noteworthy, the H1 receptor antagonist pyrilamine disrupted IA memory retrieval in rats, thus strongly supporting an active involvement of endogenous histamine; 90 min after the retention test, c-Fos-positive neurons were significantly fewer in the CA1s of a-FMHis-treated rats that displayed amnesia compared with in the control group. We also found reduced levels of phosphorylated cAMP-responsive element binding protein (pCREB) in the CA1s of a-FMHis-treated animals compared with in controls. Increases in pCREB levels are associated with retrieval of associated memories. Targeting the histaminergic system may modify the retrieval of emotional memory; hence, histaminergic ligands might reduce dysfunctional aversive memories and improve the efficacy of exposure psychotherapies.
Keywords: H1 receptor; histamine; inhibitory avoidance; memory; retrieval.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Histaminergic Neurotransmission as a Gateway for the Cognitive Effect of Oleoylethanolamide in Contextual Fear Conditioning.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017 May 1;20(5):392-399. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyw110. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28339575 Free PMC article.
-
Histamine in the basolateral amygdala promotes inhibitory avoidance learning independently of hippocampus.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 May 12;112(19):E2536-42. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1506109112. Epub 2015 Apr 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25918368 Free PMC article.
-
Histamine enhances inhibitory avoidance memory consolidation through a H2 receptor-dependent mechanism.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2006 Jul;86(1):100-6. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2006.01.001. Epub 2006 Feb 20. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2006. PMID: 16488163
-
Histamine regulates memory consolidation.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2017 Nov;145:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2017.08.007. Epub 2017 Aug 23. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2017. PMID: 28838882 Review.
-
Memory formation: the sequence of biochemical events in the hippocampus and its connection to activity in other brain structures.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 1997 Nov;68(3):285-316. doi: 10.1006/nlme.1997.3799. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 1997. PMID: 9398590 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of carbonic anhydrases in extinction of contextual fear memory.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Jul 7;117(27):16000-16008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1910690117. Epub 2020 Jun 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32571910 Free PMC article.
-
Chemogenetic activation of histamine neurons promotes retrieval of apparently lost memories.Mol Brain. 2024 Jun 15;17(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s13041-024-01111-8. Mol Brain. 2024. PMID: 38877480 Free PMC article.
-
Diet Prevents Social Stress-Induced Maladaptive Neurobehavioural and Gut Microbiota Changes in a Histamine-Dependent Manner.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 13;23(2):862. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020862. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35055048 Free PMC article.
-
Brain histamine modulates recognition memory: possible implications in major cognitive disorders.Br J Pharmacol. 2020 Feb;177(3):539-556. doi: 10.1111/bph.14478. Epub 2018 Sep 22. Br J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 30129226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histaminergic Neurotransmission as a Gateway for the Cognitive Effect of Oleoylethanolamide in Contextual Fear Conditioning.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017 May 1;20(5):392-399. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyw110. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28339575 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abel T, Lattal KM. Molecular mechanisms of memory acquisition, consolidation and retrieval. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2001;11(2):180–187. - PubMed
-
- McGaugh JL. Memory--a century of consolidation. Science. 2000;287(5451):248–251. - PubMed
-
- Szapiro G, et al. Molecular mechanisms of memory retrieval. Neurochem Res. 2002;27(11):1491–1498. - PubMed
-
- Brown R, Silva AJ. Molecular and cellular cognition; the unraveling of memory retrieval. Cell. 2004;117(1):3–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

