Global Aesthetics Consensus: Hyaluronic Acid Fillers and Botulinum Toxin Type A-Recommendations for Combined Treatment and Optimizing Outcomes in Diverse Patient Populations
- PMID: 27119917
- PMCID: PMC5242215
- DOI: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000002119
Global Aesthetics Consensus: Hyaluronic Acid Fillers and Botulinum Toxin Type A-Recommendations for Combined Treatment and Optimizing Outcomes in Diverse Patient Populations
Abstract
Background: Combination of fillers and botulinum toxin for aesthetic applications is increasingly popular. Patient demographics continue to diversify, and include an expanding population receiving maintenance treatments over decades.
Methods: A multinational panel of plastic surgeons and dermatologists convened the Global Aesthetics Consensus Group to develop updated guidelines with a worldwide perspective for hyaluronic acid fillers and botulinum toxin. This publication considers strategies for combined treatments, and how patient diversity influences treatment planning and outcomes.
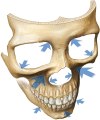
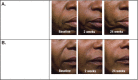
Results: Global Aesthetics Consensus Group recommendations reflect increased use of combined treatments in the lower and upper face, and some midface regions. A fully patient-tailored approach considers physiologic and chronologic age, ethnically associated facial morphotypes, and aesthetic ideals based on sex and culture. Lower toxin dosing, to modulate rather than paralyze muscles, is indicated where volume deficits influence muscular activity. Combination of toxin with fillers is appropriate for several indications addressed previously with toxin alone. New scientific data regarding hyaluronic acid fillers foster an evidence-based approach to selection of products and injection techniques. Focus on aesthetic units, rather than isolated rhytides, optimizes results from toxin and fillers. It also informs longitudinal treatment planning, and analysis of toxin nonresponders.
Conclusions: The emerging objective of injectable treatment is facial harmonization rather than rejuvenation. Combined treatment is now a standard of care. Its use will increase further as we refine the concept that aspects of aging are intimately related, and that successful treatment entails identifying and addressing the primary causes of each.
Clinical question/level of evidence: Therapeutic, V.
Figures


References
-
- Custis T, Beynet D, Carranza D, Greco J, Lask GP, Kim J. Comparison of treatment of melomental fold rhytides with cross-linked hyaluronic acid combined with onabotulinumtoxina and cross-linked hyaluronic acid alone. Dermatol Surg. 2010;36(Suppl 3):1852–1858. - PubMed
-
- Carruthers A, Carruthers J, Monheit GD, Davis PG, Tardie G. Multicenter, randomized, parallel-group study of the safety and effectiveness of onabotulinumtoxinA and hyaluronic acid dermal fillers (24-mg/ml smooth, cohesive gel) alone and in combination for lower facial rejuvenation. Dermatol Surg. 2010;36(Suppl 4):2121–2134. - PubMed
-
- Carruthers JD, Glogau RG, Blitzer A Facial Aesthetics Consensus Group Faculty. Advances in facial rejuvenation: Botulinum toxin type a, hyaluronic acid dermal fillers, and combination therapies. Consensus recommendations. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008;121(Suppl):5S–30S; quiz 31S. - PubMed
-
- Raspaldo H, Baspeyras M, Bellity P, et al. Consensus Group. Upper- and mid-face anti-aging treatment and prevention using onabotulinumtoxin A: The 2010 multidisciplinary French consensus. Part 1. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2011;10:36–50. - PubMed
-
- Raspaldo H, Niforos FR, Gassia V, et al. Consensus Group. Lower-face and neck antiaging treatment and prevention using onabotulinumtoxin A: The 2010 multidisciplinary French consensus. Part 2. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2011;10:131–149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

